That's right - when thinking about having children, don't just focus on the women's age. Think about sperm quality also. From Science Daily:
Men's sperm quality declines with age, review of 90 studies confirms
Conflicting evidence about the extent to which men's semen quality declines with age -- likely lowering their fertility -- is being cleared up by new research that has collated and reviewed data from 90 previous studies from around the world.
After conducting a systematic review and meta-analysis of the studies' data, researchers from the University's Departments of Zoology and Anatomy found consistent age-related declines in semen volume and sperm performance and increases in malformed and DNA-damaged sperm. Semen quality is regarded as a proxy for how fertile a male is.
"The effects of declining semen traits with increasing male age have largely been ignored due to inconsistencies in the literature, but our work now suggests that male age affects a variety of traits. It is well recognised that reduced sperm performance can affect pregnancy success, but it is less well known that the quality of the sperm, particularly DNA quality, could affect the development and health of the offspring," Dr Johnson says.
"Our study made no attempt to estimate the rate of decline, but some well-controlled clinic-based studies have observed consistent declines with increasing age, whereas others project declines after age 35 for some traits and after age 40 for others" she says.
"Older males contribute to increased risk of obstetric complications, miscarriage, and offspring disorders such as autism, Down syndrome, epilepsy, and schizophrenia. In addition, increasing male age may be an overlooked component of couple infertility, leading to our increased use and dependency on fertility treatments, such as IVF."
The authors suggest that clinical analysis of the percentage of DNA-fragmented sperm cells and a greater focus on how well sperm swim may lead to better patient outcomes during fertility treatments of aging couples."These are likely more accurate and consistent predictors of a man's fertility status than commonly clinically measured traits such as semen volume, sperm concentration and total sperm count," Dr Johnson says.
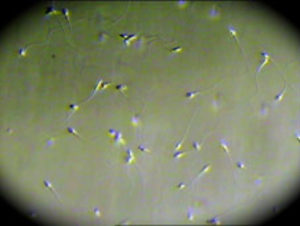 Sperm under microscope. Credit: Fertility Associates Ltd. NZ
Sperm under microscope. Credit: Fertility Associates Ltd. NZ
