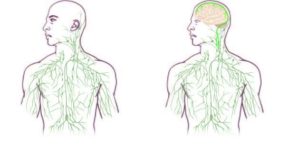
 I can't resist posting excerpts from a recent article announcing that researchers just found an entirely new lymph system ("lymphatic vessels") in the brain that transports fluid in the brain, and is probably "crucial to metabolic and inflammatory processes". The image in this post shows the system in the brain. Amazing that it is only now "discovered" - apparently it was noticed by an anatomist 2 centuries ago, but this was pooh-poohed by modern day physicians. Until now. Excerpts from the Atlantic:
I can't resist posting excerpts from a recent article announcing that researchers just found an entirely new lymph system ("lymphatic vessels") in the brain that transports fluid in the brain, and is probably "crucial to metabolic and inflammatory processes". The image in this post shows the system in the brain. Amazing that it is only now "discovered" - apparently it was noticed by an anatomist 2 centuries ago, but this was pooh-poohed by modern day physicians. Until now. Excerpts from the Atlantic:
Scientists Somehow Just Discovered a New System of Vessels in Our Brains
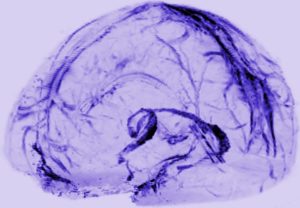
You are now among the first people to see the brain’s lymphatic system. The vessels in the photo above transport fluid that is likely crucial to metabolic and inflammatory processes. Until now, no one knew for sure that they existed. Doctors practicing today have been taught that there are no lymphatic vessels inside the skull. Those deep-purple vessels were seen for the first time in images published this week by researchers at the U.S. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
In the rest of the body, the lymphatic system collects and drains the fluid that bathes our cells, in the process exporting their waste. It also serves as a conduit for immune cells, which go out into the body looking for adversaries and learning how to distinguish self from other, and then travel back to lymph nodes and organs through lymphatic vessels.
Senior investigator Daniel Reich trained as both a neurologist and radiologist, and his expertise is in inflammatory brain disease. The connection between the immune system and the brain is at the core of what he says he spends most of his time thinking about: multiple sclerosis. The immune system appears to modulate or even underlie many neurologic diseases, and the cells of the central nervous system produce waste that needs to be washed away just like other metabolically active cells. This discovery should make it possible to study how the brain does that, how it circulates white blood cells, and how these processes may go awry in diseases or play a role in aging.
Around the same time, researchers discovered fluid in the brains of mice and humans that would become known as the “glymphatic system.” It was described by a team at the University of Rochester in 2015 as not just the brain’s “waste-clearance system,” but as potentially helping fuel thebrain by transporting glucose, lipids, amino acids, and neurotransmitters.
Wouldn’t neurosurgeons, at some point in their meticulous down-to-the-millimeter dissecting of brains, have stopped and said, “Hey ... what’s this thing?”The lymph vessels probably escaped detection because they’re inside a thick membrane, the dura mater, which is the consistency of leather. They run alongside blood vessels that are much larger, and on MRI the signal that creates the images is dominated by the blood vessels.
But this pathway appears crucial to life and health. A 2013 study in Science found that glymphatic flow seems to increase by almost double during sleep (in mice). Sleep disturbances are a common feature in Alzheimer’s and other neurologic disorders, and it’s possible that inadequate clearing of the brain’s waste products is related to exacerbating or even causing the disease....
The flow of glymphatic fluid can change based on a person’s intake of omega-3 fatty acids, a study showed earlier this year. Preliminary findings like these together suggest a pathway through which nutrition and sleep can be related to neurologic disorders. Optimizing this glymphatic flow could become a central theme for the future of neurologic health. “If all of this is true, there probably is a connection between these two systems, glymphatic and lymphatic,” Reich said. “And that would be one of the major functions of cerebrospinal fluid.”

From The Atlantic. Credit: Daniel Reich/ National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke