 What do these School Vehicle labels say about the state of education in the US? One spelling error could be an inadvertent typo, but twice? I think not.
What do these School Vehicle labels say about the state of education in the US? One spelling error could be an inadvertent typo, but twice? I think not.
Health, Microbes, and More

 What do these School Vehicle labels say about the state of education in the US? One spelling error could be an inadvertent typo, but twice? I think not.
What do these School Vehicle labels say about the state of education in the US? One spelling error could be an inadvertent typo, but twice? I think not.
 It shouldn't be a surprise that 2024 is on track to be the warmest year on record. In fact, the years 2015 to 2024 will be the warmest ten years on record globally. North America had its warmest October on record
It shouldn't be a surprise that 2024 is on track to be the warmest year on record. In fact, the years 2015 to 2024 will be the warmest ten years on record globally. North America had its warmest October on record
The World Meteorological Association also pointed that "the loss of ice from glaciers, sea-level rise, and ocean heating are accelerating". Of course, it's climate change from our addiction to oil, gas, and plastics (which are made from petrochemicals).
Yet, governments are in denial or not willing to take the necessary steps to reduce our reliance on petrochemicals. We need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, not just talk about or ignore the problem. It appears the mantra of many governments is: Burn Baby, Burn!
From World Meteorological Association: 2024 is on track to be hottest year on record as warming temporarily hits 1.5°C
The year 2024 is on track to be the warmest year on record after an extended streak of exceptionally high monthly global mean temperatures, according to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
...continue reading "This Year Will Be The Hottest On Record"
 Many people in densely populated towns very close to New York City were surprised that they could see the aurora borealis last night. It's usually hard to even see stars because of the light pollution.
Many people in densely populated towns very close to New York City were surprised that they could see the aurora borealis last night. It's usually hard to even see stars because of the light pollution.
Not the spectacular views seen in northern states, but still beautiful.

 Summer 2024 was the hottest summer on record, and this is following last summer (June through August) - which was the hottest summer globally up to that point. As you can see, the bar keeps rising.
Summer 2024 was the hottest summer on record, and this is following last summer (June through August) - which was the hottest summer globally up to that point. As you can see, the bar keeps rising.
Looking back years from now, we may view the summer of 2024 as "cool" compared to what's ahead.... Climate change, of course. The world is in uncharted territory now.
From Yale E360 (Yale School of the Environment): This Summer Was the Hottest on Record
The summer of 2024 set new records, European scientists have found. The world has never seen temperatures reach so high between June and August. ...continue reading "Summer 2024 Was the Hottest On Record"
 Dogs and their ability to detect diseases through their smelling abilities could be important in efforts to control the spread of the prion disease called chronic wasting disease (CWD). Different diseases, including CWD, have characteristic odors or scents.
Dogs and their ability to detect diseases through their smelling abilities could be important in efforts to control the spread of the prion disease called chronic wasting disease (CWD). Different diseases, including CWD, have characteristic odors or scents.
CWD is an always fatal neurologic prion disease (similar to mad cow disease) that is slowly spreading through deer,moose, and elk populations throughout the US and Canada. A recent study found that dogs trained to detect the odor of CWD were able to detect CWD in deer feces with over 80% accuracy.
Currently there is no way to detect the disease in animals before symptoms set in. The fear is that while the disease is now limited to deer, moose, and elk, it could make a cross-species jump to humans. (More information)
From CIDRAP (Center for Infectious Disease Research & Policy): Study: Dogs can detect chronic wasting disease in white-tail deer
Chronic wasting disease, a fatal prion disease found in cervids, can be detected by dogs trained to identify the scent, according to a new study published today in PLoS One. The dogs were able to identify infected deer through feces samples. ...continue reading "Dogs Can Detect The Smell of Chronic Wasting Disease"
 There has been a lot of discussion recently over whether or when the Atlantic Ocean current called Atlantic Meridional Overturning Current (AMOC) could collapse soon. The Gulf Stream is part of this current. This critically important current acts like a conveyor belt that brings warm water through the Atlantic Ocean up to the north Atlantic (Europe) and colder, saltier water down to the Southern Hemisphere.
There has been a lot of discussion recently over whether or when the Atlantic Ocean current called Atlantic Meridional Overturning Current (AMOC) could collapse soon. The Gulf Stream is part of this current. This critically important current acts like a conveyor belt that brings warm water through the Atlantic Ocean up to the north Atlantic (Europe) and colder, saltier water down to the Southern Hemisphere.
A new study predicts a collapse of the current happening soon - at some point between 2037 and 2064, but most likely before 2050. The current has been slowing down in recent years due to climate change, warming oceans, and the melting of glaciers and ice sheets.
The AMOC collapse would have devastating effects not just in Europe (it brings warm temperatures to Europe), but to the world. The AMOC keeps the Northern Hemisphere warm, the Southern Hemisphere from overheating, and distributes nutrients throughout the marine ecosystem.
One result: Arctic ice and cold would creep south in Europe and North America.
Excerpts from CNN: A critical system of Atlantic Ocean currents could collapse as early as the 2030s, new research suggests
A vital system of Atlantic Ocean currents that influences weather across the world could collapse as soon as the late 2030s, scientists have suggested in a new study — a planetary-scale disaster that would transform weather and climate. ...continue reading "Research Says Critical Ocean Currents Could Collapse In Our Lifetime"
 Uh-oh. The Earth is really warming up, and very rapidly. Sunday was the hottest day recorded globally. But then... Monday was even hotter! This means that in the space of several days, two global records were set in two days.
Uh-oh. The Earth is really warming up, and very rapidly. Sunday was the hottest day recorded globally. But then... Monday was even hotter! This means that in the space of several days, two global records were set in two days.
And it will continue to get warmer (hotter) in the coming months and years. We do know what is causing this climate change of increased global warmth - it's the burning of fossil fuels (e.g., gas, oil, coal). The big question - can humans change their ways?
From The New York Times, the Climate Newsletter: Earth’s Hottest Days Ever
Twice this week, global temperatures broke records, but scientists are more concerned about a longer-term pattern of hotter weather.
This past Sunday was the warmest single day ever recorded, according to the Copernicus Climate Change Service, the European Union-funded research organization. That is, until Monday, when global temperatures inched up a bit more. Then Monday became the hottest day in modern history, with an average global temperature of 17.16 Celsius or 62.88 Fahrenheit. Tuesday was almost as hot. ...continue reading "The Two Hottest Days On Earth Were This Week"
 It shouldn't be a surprise to read that carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are surging and accumulating faster than ever. In May, it surged to 427 parts per million (426.90 ppm) - while in 1960 it was about 320 ppm. It's depressing, and it doesn't bode well for our future.
It shouldn't be a surprise to read that carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are surging and accumulating faster than ever. In May, it surged to 427 parts per million (426.90 ppm) - while in 1960 it was about 320 ppm. It's depressing, and it doesn't bode well for our future.
These high levels of carbon dioxide are a major driver of the record-setting heat we've been experiencing in recent years. Carbon dioxide is the gas that accounts for the majority of global warming (yes, climate change) and is caused by human activities. The human activities are burning of fossil fuels, such as gas and oil - in vehicles, coal-fired plants, large industrial operations, ships, airplanes, rockets.
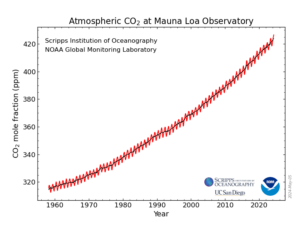
Excerpts from NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration): During a year of extremes, carbon dioxide levels surge faster than ever
Carbon dioxide is accumulating in the atmosphere faster than ever — accelerating on a steep rise to levels far above any experienced during human existence, scientists from NOAA and the Scripps Institution of Oceanography offsite link at the University of California San Diego announced today. ...continue reading "Carbon Dioxide Levels In Atmosphere Keep Rapidly Rising"
 Today is the Summer Solstice! The longest day and the shortest night of the year in the Northern Hemisphere.
Today is the Summer Solstice! The longest day and the shortest night of the year in the Northern Hemisphere.
After this, the days will get shorter and shorter. I'm not ready for that.

Forever chemicals are in the news all the time now. A very interesting and well-researched article was recently published by the investigative journalism site ProPublica about Kris Hansen, a chemistry PhD who worked at 3M company. Initially, as part of her job in 1997, she documented that forever chemicals (PFOS, PFAS) were showing up in everyone's blood - both workers at the company, as well as people outside the company. Animals also. But then her work was suppressed, her bosses at 3M convinced her the chemicals were safe, and she continued working there for years.
Also... she was sidelined by her bosses after her initial findings, her job became more limited at the company, and finally she moved to a different area of the company (medical devices). Yet for years she told her husband and herself that the chemicals were safe. Only in 2021, after watching a John Oliver segment on TV about forever chemicals, she finally googled PFOS. But she only left the company in 2022 (after 26 years) when her job was eliminated.
One interesting part to me was - How did she rationalize doing nothing and continue working there for decades? She knew it was appearing in everyone's blood, there was research (animal and human) available showing it caused harms, and yet.... she chose to believe what management was saying (it's safe), stayed silent, and basically buried her head in the sand. Didn't want to know...
Yes, I've seen this elsewhere - when interacting with people in higher level white collar jobs in the pesticide industry. Their salaries are good, their jobs depend on denialism and ignoring scientific research, and so they spout the industry line of "it's safe"..."nothing is proven". So it continues...
A few excerpts from ProPublica: Toxic Gaslighting: How 3M Executives Convinced a Scientist the Forever Chemicals She Found in Human Blood Were Safe
The next morning, anxious to see the results, Hansen arrived at the lab before anyone else. For the first time since she had begun testing blood, some of the samples showed no trace of PFOS. She was so struck that she called her husband. There was nothing wrong with her equipment or methodology; PFOS, a man-made chemical produced by her employer, really was in human blood, practically everywhere. ...continue reading "Denialism and Cover-up At Manufacturer Of Forever Chemicals"