 New research further confirms a link between higher lutein levels (as measured in the blood) and the preservation of "crystallized intelligence" in older adults. Crystallized intelligence is the ability to use the skills and knowledge one has acquired over a lifetime. Lutein is in foods such as leafy green vegetables, cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and cabbage) and egg yolks. Lutein is also found in small amounts in other fruits and vegetables. Bottom line: eat a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables daily. [Original study.]Medical Xpress:
New research further confirms a link between higher lutein levels (as measured in the blood) and the preservation of "crystallized intelligence" in older adults. Crystallized intelligence is the ability to use the skills and knowledge one has acquired over a lifetime. Lutein is in foods such as leafy green vegetables, cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, brussels sprouts, cauliflower, and cabbage) and egg yolks. Lutein is also found in small amounts in other fruits and vegetables. Bottom line: eat a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables daily. [Original study.]Medical Xpress:
Study links nutrition to brain health and intelligence in older adults
A study of older adults links consumption of a pigment found in leafy greens to the preservation of "crystallized intelligence," the ability to use the skills and knowledge one has acquired over a lifetime.
Lutein (LOO-teen) is one of several plant pigments that humans acquire through the diet, primarily by eating leafy green vegetables, cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, or egg yolks, said University of Illinois graduate student Marta Zamroziewicz, who led the study with Illinois psychology professor Aron Barbey. Lutein accumulates in the brain, embedding in cell membranes, where it likely plays "a neuroprotective role," she said. "Previous studies have found that a person's lutein status is linked to cognitive performance across the lifespan," Zamroziewicz said.
The study enrolled 122 healthy participants aged 65 to 75 who solved problems and answered questions on a standard test of crystallized intelligence. Researchers also collected blood samples to determine blood serum levels of lutein and imaged participants' brains using MRI to measure the volume of different brain structures. The team focused on parts of the temporal cortex, a brain region that other studies suggest plays a role in the preservation of crystallized intelligence.
The researchers found that participants with higher blood serum levels of lutein tended to do better on tests of crystallized intelligence. Serum lutein levels reflect only recent dietary intakes, Zamroziewicz said, but are associated with brain concentrations of lutein in older adults, which reflect long-term dietary intake. Those with higher serum lutein levels also tended to have thicker gray matter in the parahippocampal cortex, a brain region that, like crystallized intelligence, is preserved in healthy aging, the researchers report..... "Our findings do not demonstrate causality," Zamroziewicz said. "We did find that lutein is linked to crystallized intelligence through the parahippocampal cortex."

 A big concern nowadays is why some children develop autism, specifically autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Autism spectrum disorder is considered a life-long neurodevelopmental disorder that is thought to affect 1 out of 68 American children. While the causes of ASD are unknown in most cases, some studies report an association (higher risk) between a pregnant woman's infections and fever during pregnancy and risk of ASD in the baby, while other studies don't find such an association. Some studies also looked at the
A big concern nowadays is why some children develop autism, specifically autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Autism spectrum disorder is considered a life-long neurodevelopmental disorder that is thought to affect 1 out of 68 American children. While the causes of ASD are unknown in most cases, some studies report an association (higher risk) between a pregnant woman's infections and fever during pregnancy and risk of ASD in the baby, while other studies don't find such an association. Some studies also looked at the  This study found impressive results - improvement in autistic behaviors in children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) with four months of daily vitamin D supplementation. Children in the
This study found impressive results - improvement in autistic behaviors in children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) with four months of daily vitamin D supplementation. Children in the  Interesting preliminary research that suggests that daily intake for 12 weeks of several beneficial bacteria species (Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. casei, L. fermentum, and Bifidobacterium bifidum) resulted in improved mental (cognitive) functioning in 52 people with Alzheimer's Disease. Could this be true - daily probiotics to improve mental functioning in those with Alzheimer's?
Interesting preliminary research that suggests that daily intake for 12 weeks of several beneficial bacteria species (Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. casei, L. fermentum, and Bifidobacterium bifidum) resulted in improved mental (cognitive) functioning in 52 people with Alzheimer's Disease. Could this be true - daily probiotics to improve mental functioning in those with Alzheimer's? Eating lots of fruits and vegetables (more than 10 servings a day!) is linked to better cognitive functioning in both normal weight and overweight adults (both young and older adults), and may delay the onset of cognitive decline that occurs with aging and also dementia.
Eating lots of fruits and vegetables (more than 10 servings a day!) is linked to better cognitive functioning in both normal weight and overweight adults (both young and older adults), and may delay the onset of cognitive decline that occurs with aging and also dementia. 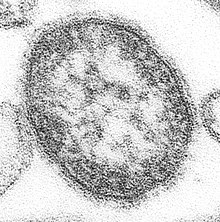 An electron micrograph of the measles virus.
An electron micrograph of the measles virus.  Child showing a 4-day measles rash.
Child showing a 4-day measles rash.  Another study finding brain changes from playing tackle football - this time measurable brain changes were found in boys 8 to 13 years old after just one season of playing football. None of the boys had received a concussion diagnosis during the season. The changes in the white matter of the brain (and detected with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were from the cumulative subconcussive head impacts that occur in football - the result of repetitive hits to the head during games and practices.
Another study finding brain changes from playing tackle football - this time measurable brain changes were found in boys 8 to 13 years old after just one season of playing football. None of the boys had received a concussion diagnosis during the season. The changes in the white matter of the brain (and detected with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were from the cumulative subconcussive head impacts that occur in football - the result of repetitive hits to the head during games and practices. Lead exposure is a big problem for children throughout the United States and the rest of the world - whether lead from plumbing, lead paint, lead solder, and even from nearby mining. There are no safe levels of lead in children (best is zero) because it is a neurotoxicant - thus it can permanently lower IQ scores as well as other neurological effects. More lead gets absorbed if the person also has an iron deficiency than if the person has normal iron levels.
Lead exposure is a big problem for children throughout the United States and the rest of the world - whether lead from plumbing, lead paint, lead solder, and even from nearby mining. There are no safe levels of lead in children (best is zero) because it is a neurotoxicant - thus it can permanently lower IQ scores as well as other neurological effects. More lead gets absorbed if the person also has an iron deficiency than if the person has normal iron levels. More great news about drinking coffee daily - for women. Older women (between ages of 65 to 80 at the start of the study) reporting drinking higher amounts of caffeinated beverages (about 261 mg which is about 2 to 3 cups of coffee per day) had a lower incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment over a 10 year period (as compared to the low caffeine group). The low caffeine group averaged 64 mg of caffeine per day. Other studies also found a reduction in "cognitive decline" in older people with coffee consumption. This study, among others, is more evidence of caffeine being "neuroprotective". NOTE: an 8-ounce cup of brewed coffee contains about 95 mg of caffeine, 8-ounces of brewed black tea contains about 47 mg, a 12-ounce can of carbonated cola contains 33 mg, and 8-ounces of decaffeinated coffee has about 5 mg of caffeine. Science Daily:
More great news about drinking coffee daily - for women. Older women (between ages of 65 to 80 at the start of the study) reporting drinking higher amounts of caffeinated beverages (about 261 mg which is about 2 to 3 cups of coffee per day) had a lower incidence of dementia and cognitive impairment over a 10 year period (as compared to the low caffeine group). The low caffeine group averaged 64 mg of caffeine per day. Other studies also found a reduction in "cognitive decline" in older people with coffee consumption. This study, among others, is more evidence of caffeine being "neuroprotective". NOTE: an 8-ounce cup of brewed coffee contains about 95 mg of caffeine, 8-ounces of brewed black tea contains about 47 mg, a 12-ounce can of carbonated cola contains 33 mg, and 8-ounces of decaffeinated coffee has about 5 mg of caffeine. Science Daily: