 It is very exciting whenever a study has good results in preventing cancer, especially if this is from simply eating certain foods. This recently occurred in a large study of people with a high hereditary susceptibility to certain cancers, called Lynch syndrome.
It is very exciting whenever a study has good results in preventing cancer, especially if this is from simply eating certain foods. This recently occurred in a large study of people with a high hereditary susceptibility to certain cancers, called Lynch syndrome.
The study found that just eating some resistant starch (e.g., the amount in a green tipped banana) daily was enough to cut the incidence of upper GI cancers (e.g., pancreatic, bile duct, stomach, and duodenal cancers) by 60% over the next ten years. These are fabulous results.
However, it did not have an effect on the incidence of colorectal cancer and endometrial cancer.
In the well-done study (conducted in England, Wales, and Finland), people were randomly assigned to either a group that ate 30 grams of resistant starch daily or a placebo daily for up to 4 years. Then they were all followed for up to a further 10 years, and a portion up to 20 years. [Note: the researchers said the 30 g daily was equivalent to one slightly green banana]
Resistant starch is a type of dietary fiber found in foods such as slightly green bananas, potatoes, whole grains, beans, chickpeas, lentils, and seeds. Resistant starch is not digested in the small intestine, but is fermented by gut microbes to produce beneficial short-chain fatty acids, such as butyrate, in the colon (large bowel).
Bottom line: Eat a variety of fiber rich foods (whole grains, legumes, fruits, vegetables, seeds, and nuts) daily, including foods that provide resistant starch. Your gut microbes and health will thank you!
From Science Daily: Cancer study: Major preventive effect from resistant starch in people with Lynch syndrome
A trial in people with high hereditary risk of a wide range of cancers has shown a major preventive effect from resistant starch, found in a wide range of foods such as oats, breakfast cereal, cooked and cooled pasta or rice, peas and beans and slightly green bananas.
...continue reading "Preventing Cancers By Eating Foods Containing Resistant Starch"

 The Paleo diet has been around for years and yet it continues to be controversial. The debate is whether following the Paleo diet long-term has health benefits or not? Supporters of the Paleo (Paleolothic) diet say it promotes gut health and is good for gut microbes, but
The Paleo diet has been around for years and yet it continues to be controversial. The debate is whether following the Paleo diet long-term has health benefits or not? Supporters of the Paleo (Paleolothic) diet say it promotes gut health and is good for gut microbes, but 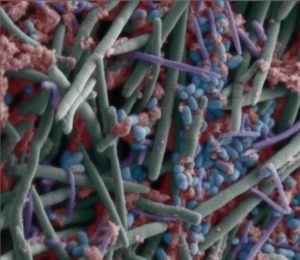 Gut bacteria in children varies among different Asian countries. A
Gut bacteria in children varies among different Asian countries. A