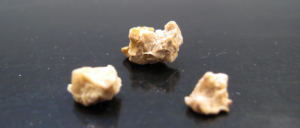
The incidence of kidney stones is on the rise worldwide, with 1 in 11 people expected to develop a stone at some point. There are several subtypes of kidney stones, with calcium oxalate (CaOx) stones occurring in more than 70% of cases. Recent research found live bacteria in calcium oxalate stones, along with biofilms.
Biofilms are communities of bacteria sticking to one another and coated with a protective slime. In these kidney stones, the biofilms were in-between mineral layers. Several bacterial species were most common in the kidney stones: E. faecalis, P. mirabilis, and E. coli.
Prior to this study, calcium oxalate kidney stones were not considered bacterial. The researchers thought that the bacteria might explain why people tend to have recurrent kidney stones.
Kidney stones begin as tiny crystals that can accumulate and clump together in urine. One easy way to decrease risk of developing kidney stones is do drink plenty of water (want to dilute your urine). Low fluid intake and dehydration is associated with increased kidney stone formation, due to concentrated urine.
An interesting earlier study looked at the microbiome of the kidneys and found that the beneficial bacteria L. crispatus is found in the absence of kidney stones, while the presence of E.coli was associated with the development of kidney stones. The researchers found that the L. crispatus somehow blocked E.coli's ability to form kidney stones.
From Medical Xpress: Previously unknown bacterial component in kidney stone formation discovered
In an unexpected finding, a UCLA-led team has discovered that bacteria are present inside the most common type of kidney stone, revealing a previously unrecognized component involved in their formation. ...continue reading "Bacteria Found In Kidney Stones"


 Scientists have long known about some factors linked to a higher risk of developing multiple sclerosis (MS).These include low levels of sunlight exposure, low vitamin D blood levels, smoking, and being infected with the Epstein Barr virus in adolescence and adulthood (infectious mononucleosis). Recent
Scientists have long known about some factors linked to a higher risk of developing multiple sclerosis (MS).These include low levels of sunlight exposure, low vitamin D blood levels, smoking, and being infected with the Epstein Barr virus in adolescence and adulthood (infectious mononucleosis). Recent  The microbes in your mouth may offer a clue to obesity. New
The microbes in your mouth may offer a clue to obesity. New 
 Very depressing news. The EPA plans to NOT take into account of the value of human life any more when making rules and setting policy regarding air pollutants (e.g., fine particulate matter and ozone). Meaning
Very depressing news. The EPA plans to NOT take into account of the value of human life any more when making rules and setting policy regarding air pollutants (e.g., fine particulate matter and ozone). Meaning 