 The last post pointed out that the importance of high levels of physical activity or exercise in reducing the risk of 5 diseases. Now a study points out that all this exercise (starting at about 3 to 5 hours of exercise per week) can result in the heart becoming enlarged from all this exercise ("athlete's heart"), and that this is totally normal and healthy. The researchers also stressed that doctors should be aware that athlete's heart or "exercise-related cardiac remodeling" can occur not only in professional athletes, but also in those engaging in moderate levels of exercise, and that it not be misdiagnosed as heart disease. From Science Daily:
The last post pointed out that the importance of high levels of physical activity or exercise in reducing the risk of 5 diseases. Now a study points out that all this exercise (starting at about 3 to 5 hours of exercise per week) can result in the heart becoming enlarged from all this exercise ("athlete's heart"), and that this is totally normal and healthy. The researchers also stressed that doctors should be aware that athlete's heart or "exercise-related cardiac remodeling" can occur not only in professional athletes, but also in those engaging in moderate levels of exercise, and that it not be misdiagnosed as heart disease. From Science Daily:
Regular exercise can lead to heart disease misdiagnosis
Scientists have shown that people who exercise for even a few hours each week can enlarge their hearts. This is a normal and beneficial response to exercise, but until now has only been recognised in athletes. The researchers say that doctors should now consider an individual's activity level before diagnosing common heart conditions.
"It's well known that the hearts of endurance athletes adapt in response to exercise, a phenomenon called 'athlete's heart'. This study is the first to show that healthy adults who do regular exercise may also develop enlarged hearts. As a result, there's a risk that some active adults could be misdiagnosed with heart disease," says Declan O'Regan, of the MRC Clinical Sciences Centre, based at Imperial College London, and one of the lead scientists on the research. The findings were published today in Circulation: Cardiovascular Imaging.
Scientists have not previously known the extent to which the hearts of healthy people adapt to the demands of moderate exercise. Over 1000 people took part in this study, making it one of the largest of its kind. Participants selected one of four possible categories that best represented their activity level over the past year, according to how many hours of exercise they did each week. Around one third of participants reported doing three to five hours of exercise, and the scientists found that one in five of these people had developed an enlarged heart as a result. Similar adaptations were seen in almost half of those who reported doing more than five hours of exercise.
The findings suggest that above a threshold of three hours, the more exercise you do, the more your heart is likely to adapt, and the more the exercise, the more pronounced the changes. "Going to the gym frequently increases the thickness of your heart muscle and the volume of your heart chambers, particularly the right ventricle. It's a completely normal, healthy response. It shouldn't be misdiagnosed as being heart disease," says O'Regan. These adaptations allow the heart to pump more blood, which helps to supply exercising muscles with the oxygen and nutrients they need. Changes to the heart's thickness and volume happen in tandem, and this distinguishes them from the changes seen in disease, which occur in isolation.
Today, doctors across the world use a standard of set values to see if the thickness and volume of a person's heart fall into the healthy or abnormal range. This helps to ensure consistency between different hospitals. According to O'Regan, the data that underpins these ranges comes from a relatively small study with people who were mainly sedentary. He says, "In this latest study, we looked at a much larger and broader group of people. We found that more people reported being active than had done in previous studies. Our recommendations reflect this growing participation in exercise.".....And this interesting research shows that even moderate physical activity is associated with changes in the heart's size and shape, which are visible on a cardiac MRI.

 Get active, really active, to reduce your risk for 5 diseases: breast cancer, colon cancer, heart disease, and ischemic stroke. Instead of the 150 minutes of brisk walking or 75 minutes per week of running (which is equal to the 600 metabolic equivalent (MET) minutes now recommended by the World Health Organization), this study found that much more exercise is needed for
Get active, really active, to reduce your risk for 5 diseases: breast cancer, colon cancer, heart disease, and ischemic stroke. Instead of the 150 minutes of brisk walking or 75 minutes per week of running (which is equal to the 600 metabolic equivalent (MET) minutes now recommended by the World Health Organization), this study found that much more exercise is needed for 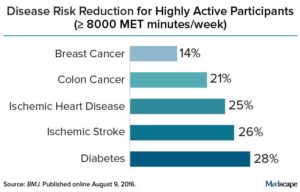 Credit: Medscape
Credit: Medscape Another interesting study looking at whether being overweight is linked to premature death, heart attacks, and diabetes. This study looked at sets of twins, in which one is heavier than the other, and followed them long-term (average 12.4 years) and found that NO - being overweight or obese (as measured by Body Mass Index or BMI) is NOT associated with premature death or heart attack (myocardial infarction), but it is associated with higher rates of type 2 diabetes. These results are in contrast with what
Another interesting study looking at whether being overweight is linked to premature death, heart attacks, and diabetes. This study looked at sets of twins, in which one is heavier than the other, and followed them long-term (average 12.4 years) and found that NO - being overweight or obese (as measured by Body Mass Index or BMI) is NOT associated with premature death or heart attack (myocardial infarction), but it is associated with higher rates of type 2 diabetes. These results are in contrast with what  Studies have found that increased nut consumption has been associated with
Studies have found that increased nut consumption has been associated with  Yup, according to a new mega-study, being overweight or obese is linked to higher risk of dying prematurely than being normal weight. And the more you weigh, the greater the risk.
Yup, according to a new mega-study, being overweight or obese is linked to higher risk of dying prematurely than being normal weight. And the more you weigh, the greater the risk.  Previous research on the health benefits of eating fish, fish oil supplements, and other sources of omega-3 fatty acids has shown mixed
Previous research on the health benefits of eating fish, fish oil supplements, and other sources of omega-3 fatty acids has shown mixed  A second study was just published about the benefits of eating whole grains daily - again a significantly lower risk of premature death, and again the effects were dose-related. That is, the more whole grains eaten daily, the lower the risk of early death. Like the
A second study was just published about the benefits of eating whole grains daily - again a significantly lower risk of premature death, and again the effects were dose-related. That is, the more whole grains eaten daily, the lower the risk of early death. Like the  New research looked at people who "aged successfully" over a 10 year period compared with those who were "suboptimal agers" or had died. The successful agers were less likely to smoke, and have higher intakes of fiber from fruits, breads, and cereals (primarily from rolled oats and whole grain breads), but not from vegetables. Successful aging was defined as including an absence of disability, depressive symptoms, cognitive impairment, respiratory symptoms, and chronic diseases including cancer, coronary artery disease, and stroke.
New research looked at people who "aged successfully" over a 10 year period compared with those who were "suboptimal agers" or had died. The successful agers were less likely to smoke, and have higher intakes of fiber from fruits, breads, and cereals (primarily from rolled oats and whole grain breads), but not from vegetables. Successful aging was defined as including an absence of disability, depressive symptoms, cognitive impairment, respiratory symptoms, and chronic diseases including cancer, coronary artery disease, and stroke.