The following is a list of nutrients that some researchers (from the Institute of Food Technology) think of as especially beneficial to the brain. Other researchers may (or probably will) focus on other nutrients. I am posting it even though I generally dislike articles that talk about "superfoods" or an itemized list of foods that one should eat to the exclusion of others. Because, of course, focusing on some nutrients may leave out many just as important nutrients.
Also, medical thinking changes over time and what was once considered "unhealthy" may later be considered a wonderful food (remember when eggs, nuts, and coconuts were almost considered evil?). And vice versa (remember when margarine with partially hydrogeneated oils and trans-fats was considered healthier than butter?) And study after study says it is better to eat the foods, rather than take supplements. So keep in mind that the following nutrients are found in whole foods and in a varied diet. And when they mention a specific food such as blueberries, remember that ALL berries have benefits (though they vary), so eat a variety of berries. Same with nuts - eat a variety and not just walnuts. From Science Daily:
Eight nutrients to protect the aging brain
Brain health is the second most important component in maintaining a healthy lifestyle according to a 2014 AARP study. As people age they can experience a range of cognitive issues from decreased critical thinking to dementia and Alzheimer's disease. In the March issue of Food Technology published by the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT), contributing editor Linda Milo Ohr writes about eight nutrients that may help keep your brain in good shape.
1. Cocoa Flavanols: Cocoa flavanols have been linked to improved circulation and heart health, and preliminary research shows a possible connection to memory improvement as well. A study showed cocoa flavanols may improve the function of a specific part of the brain called the dentate gyrus, which is associated with age-related memory (Brickman, 2014). {NOTE: good sources are cocoa and dark chocolate}
2. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids have long been shown to contribute to good heart health are now playing a role in cognitive health as well....Foods rich in omega-3s include salmon, flaxseed oil, and chia seeds.
3. Phosphatidylserine and Phosphatidic Acid: Two pilot studies showed that a combination of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidic acid can help benefit memory, mood, and cognitive function in the elderly (Lonza, 2014). {NOTE: good sources are fish and meat}
4. Walnuts: A diet supplemented with walnuts may have a beneficial effect in reducing the risk, delaying the onset, or slowing the progression of Alzheimer's disease in mice (Muthaiyah, 2014).
5. Citicoline: Citicoline is a natural substance found in the body's cells and helps in the development of brain tissue, which helps regulate memory and cognitive function, enhances communication between neurons, and protects neural structures from free radical damage.... {NOTE: Citocoline is synthesized in the body from choline, so see foods high in choline}
6. Choline: Choline, which is associated with liver health and women's health, also helps with the communication systems for cells within the brain and the rest of the body. Choline may also support the brain during aging and help prevent changes in brain chemistry that result in cognitive decline and failure. A major source of choline in the diet are eggs. { NOTE: Good sources of choline are eggs, meat, fish, beans, and cruciferous vegetables.}
7. Magnesium: Magnesium supplements are often recommended for those who experienced serious concussions. Magnesium-rich foods include avocado, soy beans, bananas and dark chocolate.
8. Blueberries: Blueberries are known to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity because they boast a high concentration of anthocyanins, a flavonoid that enhances the health-promoting quality of foods. Moderate blueberry consumption could offer neurocognitive benefits such as increased neural signaling in the brain centers.
 You can deceive yourself by calling yourself "big-boned" or "hefty", but your urine doesn't lie! Researchers found 29 biological markers in urine that are associated with body mass. These biological markers in urine are a "metabolic signature" of obesity. Note: Body mass index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight that applies to adult men and women. From Medical Xpress:
You can deceive yourself by calling yourself "big-boned" or "hefty", but your urine doesn't lie! Researchers found 29 biological markers in urine that are associated with body mass. These biological markers in urine are a "metabolic signature" of obesity. Note: Body mass index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight that applies to adult men and women. From Medical Xpress:
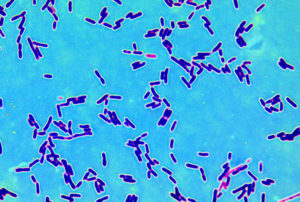 This nice general summary of what scientists know about the microbial community within us was just published by a division of the NIH (National Institutes of Health). Very simple and basic. From the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS):
This nice general summary of what scientists know about the microbial community within us was just published by a division of the NIH (National Institutes of Health). Very simple and basic. From the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS): Another study finding negative effects of air pollution - this time high levels of traffic-related air pollution is linked to slower cognitive development among 7 to 10 year old children in Barcelona, Spain. From Science Daily:
Another study finding negative effects of air pollution - this time high levels of traffic-related air pollution is linked to slower cognitive development among 7 to 10 year old children in Barcelona, Spain. From Science Daily: Long-term air pollution can cause damage to the brain: covert brain infarcts ("silent strokes") and smaller brain volume (equal to one year of brain aging).
Long-term air pollution can cause damage to the brain: covert brain infarcts ("silent strokes") and smaller brain volume (equal to one year of brain aging). Well worth reading in its entirety. In summary: Anyone who is physically capable of activity should try to reach at least 150 minutes of physical activity per week (walking is good) and have around 20 to 30 minutes of that be vigorous activity. This significantly lowers the risk of dying prematurely. (NOTE: the second study mentioned was in the April 8, 2015 post:
Well worth reading in its entirety. In summary: Anyone who is physically capable of activity should try to reach at least 150 minutes of physical activity per week (walking is good) and have around 20 to 30 minutes of that be vigorous activity. This significantly lowers the risk of dying prematurely. (NOTE: the second study mentioned was in the April 8, 2015 post: