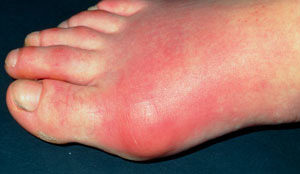
 Gout is something that is not discussed that much, but it has been increasing in recent years and now afflicts about 3.9% of adults in the US. Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis, characterized by recurrent attacks of pain, tenderness, and swelling of a joint, frequently the joint of the big toe. It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood (known as hyperuricaemia).
Gout is something that is not discussed that much, but it has been increasing in recent years and now afflicts about 3.9% of adults in the US. Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis, characterized by recurrent attacks of pain, tenderness, and swelling of a joint, frequently the joint of the big toe. It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood (known as hyperuricaemia).
Gout occurs more commonly in men ages 40 and older, who eat a lot of meat and seafood, drink a lot of alcohol (especially beer) or sweetened drinks, have high blood pressure, metabolic syndrome, or are overweight. Gout used to be known as "the disease of kings" or "rich man's disease". [On the other hand, past research has shown that consumption of coffee, cherries, vitamin C foods, and dairy products, losing weight and physical fitness seems to decrease the risk.]
Recent research showed that the DASH diet reduces blood pressure and reduces uric acid in the blood, which is why a research team (study in The BMJ) now looked at whether it lowers the risk of gout. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension or DASH diet is high in fruit, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and low-fat dairy, and low in red and processed meats, salt, and sugary drinks. On the other hand, the typical Western diet has higher intakes of red and processed meats, sweetened beverages, sweets, desserts, French fries, and refined grains. The researchers analysed data on a total of 44,444 male health professionals, who had no history of gout at the start of the study. During the 26 years of the observational study, they documented 1731 cases of gout.
The researchers found that eating a more DASH type diet - a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, whole grains, and low in salt, sugary drinks, and red and processed meats, is associated with a lower risk of gout. On the other hand, a more 'Western' diet is associated with a higher risk of gout. They found that the effects are dose dependent - the more DASH-type diet, the lower the risk of gout. Bottom line: Once again, eating lots of fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, and whole grains is linked to health benefits. From Science Daily:
Diet rich in fruit, vegetables and whole grains may lower risk of gout
A diet rich in fruit and vegetables, nuts and whole grains and low in salt, sugary drinks, and red and processed meats, is associated with a lower risk of gout, whereas a typical 'Western' diet is associated with a higher risk of gout, finds a study published by The BMJ.
Gout is a joint disease which causes extreme pain and swelling. It is most common in men aged 40 and older and is caused by excess uric acid in the blood (known as hyperuricaemia) which leads to uric acid crystals collecting around the joints. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet reduces blood pressure and is recommended to prevent heart disease. It has also been found to lower uric acid levels in the blood. Therefore, the DASH diet may lower the risk of gout.
To investigate this further, a team of US and Canada based researchers examined the relationship between the DASH and Western dietary patterns and the risk of gout. They analysed data on over 44,000 men aged 40 to 75 years with no history of gout who completed detailed food questionnaires in 1986 that was updated every four years through to 2012.
Each participant was assigned a DASH score (reflecting high intake of fruits, vegetables, nuts and legumes, such as peas, beans and lentils, low-fat dairy products and whole grains, and low intake of salt, sweetened beverages, and red and processed meats) and a Western pattern score (reflecting higher intake of red and processed meats, French fries, refined grains, sweets and desserts). During 26 years of follow-up, a higher DASH score was associated with a lower risk for gout, while a higher Western pattern was associated with an increased risk for gout.
 Gout. Credit: NHS in the UK
Gout. Credit: NHS in the UK
 Want to improve your odds of not getting a chronic disease, such as heart disease or diabetes? A recent study found that following any healthy dietary pattern, whether Mediterranean or DASH or Diabetes Risk Reduction Diet or other similar healthy dietary styles, are all linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases.
Want to improve your odds of not getting a chronic disease, such as heart disease or diabetes? A recent study found that following any healthy dietary pattern, whether Mediterranean or DASH or Diabetes Risk Reduction Diet or other similar healthy dietary styles, are all linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases.
 Another study finding more benefits of exercise was recently published in the journal Neurology.
Another study finding more benefits of exercise was recently published in the journal Neurology.  A number of recent studies and articles have discussed the effectiveness of diet in treating or preventing depression with the main conclusion that yes, it helps. Now an observational study (that will be presented in April) found that elderly people following the DASH diet most closely were 11% less likely to become depressed over time than those that did not.
A number of recent studies and articles have discussed the effectiveness of diet in treating or preventing depression with the main conclusion that yes, it helps. Now an observational study (that will be presented in April) found that elderly people following the DASH diet most closely were 11% less likely to become depressed over time than those that did not. Gout is something that is not discussed that much, but it has been increasing in recent years and now afflicts about 3.9% of adults in the US. Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis, characterized by recurrent attacks of pain, tenderness, and swelling of a joint, frequently the joint of the big toe. It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood (known as hyperuricaemia).
Gout is something that is not discussed that much, but it has been increasing in recent years and now afflicts about 3.9% of adults in the US. Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis, characterized by recurrent attacks of pain, tenderness, and swelling of a joint, frequently the joint of the big toe. It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood (known as hyperuricaemia).