 The spice turmeric is very popular these days, especially because studies link it to various health benefits. But is this true? Is it better to eat turmeric in foods or take it in pill form as a supplement? Today's post is about a study that was done by the BBC teaming up with researchers at Newcastle University (in the UK) where they looked at whether modest doses of turmeric had health benefits when ingested daily for 6 weeks. Specifically, they looked at what turmeric does to various blood markers thought to be associated with inflammation and changes that could eventually lead to the onset of cancer. It is currently thought that many or turmeric's supposed health benefits come from the compound curcumin found in it.
The spice turmeric is very popular these days, especially because studies link it to various health benefits. But is this true? Is it better to eat turmeric in foods or take it in pill form as a supplement? Today's post is about a study that was done by the BBC teaming up with researchers at Newcastle University (in the UK) where they looked at whether modest doses of turmeric had health benefits when ingested daily for 6 weeks. Specifically, they looked at what turmeric does to various blood markers thought to be associated with inflammation and changes that could eventually lead to the onset of cancer. It is currently thought that many or turmeric's supposed health benefits come from the compound curcumin found in it.
The researchers took blood samples of 100 volunteers, who were then split up into 3 groups (turmeric powder, a turmeric pill, or a placebo pill daily). Only the group that ingested turmeric in powder form (1 teaspoon mixed in food) showed changes after 6 weeks, and they were exciting beneficial changes in the methylation of DNA. This is because "methylation of the DNA can ‘go wrong’ and this can cause cells to become cancerous".
It's still early days in this research, and more has to be done, but it is exciting. In the meantime, don't take turmeric in pill form, but eat it in foods. It seems that more of the turmeric gets absorbed when eaten with foods, especially foods with fat, and also with a little black pepper. Excerpts from the article written by Michael Mosley, one of the presenters of the broadcast show "Trust Me, I'm A Doctor", from the BBC News:
Could turmeric really boost your health?
Turmeric is a spice which in its raw form looks a bit like ginger root, but when it's ground down you get a distinctive yellowy orange powder that's very popular in South Asian cuisine.....So we tracked down leading researchers from across the country and with their help recruited nearly 100 volunteers from the North East to do a novel experiment. Few of our volunteers ate foods containing turmeric on a regular basis.
Then we divided them into three groups. We asked one group to consume a teaspoon of turmeric every day for six weeks, ideally mixed in with their food. Another group were asked to swallow a supplement containing the same amount of turmeric, and a third group were given a placebo, or dummy pill. The volunteers who were asked to consume a teaspoon of turmeric a day were ingenious about what they added it to, mixing it with warm milk or adding it to yoghurt. Not everyone was enthusiastic about the taste, with comments ranging from "awful" to "very strong and lingering".
But what effect was eating turmeric having on them? We decided to try and find out using a novel test developed at University College, London, by Prof Martin Widschwendter and his team....There are at least 200 different compounds in turmeric, but there's one that scientists are particularly interested in. It gives this spice its colour. It's called curcumin. Thousands of scientific papers have been published looking at turmeric and curcumin in the laboratory - some with promising results. But they've mainly been done in mice, using unrealistically high doses. There have been few experiments done in the real world, on humans.
Prof Widschwendter is not particularly interested in turmeric but he is interested in how cancers start. His team have been comparing tissue samples taken from women with breast cancer and from women without it and they've found a change that happens to the DNA of cells well before they become cancerous. The change is in the "packaging" of the genes. It's called DNA methylation. It's a bit like a dimmer switch that can turn the activity of the gene up or down. The exciting thing is that if it is detected in time this change can, potentially, be reversed, before the cell turns cancerous.
So we asked Prof Widschwendter whether testing the DNA methylation patterns of our volunteers' blood cells at the start and end of the experiment would reveal any change in their risk of cancer and other diseases, like allergies. It was something that had not been done before. Fortunately he was very enthusiastic. "We were delighted," he said, "to be involved in this study, because it is a proof of principle study that opens entirely new windows of opportunity to really look into how we can predict preventive measures, particularly for cancer."
So what, if anything, happened? When I asked him that, he pulled out his laptop and slowly began to speak."We didn't find any changes in the group taking the placebo," he told me. That was not surprising. "The supplement group also didn't also show any difference," he went on. That was surprising and somewhat disappointing.
"But the group who mixed turmeric powder into their food," he continued, "there we saw quite substantial changes. It was really exciting, to be honest. We found one particular gene which showed the biggest difference. And what's interesting is that we know this particular gene is involved in three specific diseases: depression, asthma and eczema, and cancer. This is a really striking finding."
It certainly is. But why did we see changes only in those eating turmeric, not in those taking the same amount as a supplement? Dr Kirsten Brandt, who is a senior lecturer at Newcastle University and who helped run the experiment, thinks it may have something to do with the way the turmeric was consumed. "It could be," she told me, "that adding fat or heating it up makes the active ingredients more soluble, which would make it easier for us to absorb the turmeric.....She also told me, because our volunteers all tried consuming their turmeric in different ways, that we can be confident it was the turmeric that was making the difference and not some other ingredient used to make, say, chicken tikka masala. There is a lot more research that needs to be done, including repeating the experiment to see if these findings can be confirmed.
More information about the study and results from BBC News: Does turmeric really help protect us from cancer?

 We all know that exercise is beneficial for health. Research suggests that exercising out in nature is best for several varied reasons - including that it
We all know that exercise is beneficial for health. Research suggests that exercising out in nature is best for several varied reasons - including that it  Ten chemicals suspected or known to harm human health are present in more than 90% of U.S. household dust samples, according to a new study. The research adds to a growing body of evidence showing the dangers posed by exposure to chemicals we are exposed to on a daily basis. The chemicals come from a variety of household goods, including toys, cosmetics, personal care products, furniture, electronics, nonstick cookware, food packaging, floor coverings, some clothing (e.g., stain resistant), building materials, and cleaning products. How do the chemicals get into the dust? The chemicals can leach, migrate, abrade, or off-gas from the products, which winds up in the dust and results in human exposure. (That's right: vacuum a lot and wash your hands a lot, and try to avoid or cut back use of products with these chemicals,)
Ten chemicals suspected or known to harm human health are present in more than 90% of U.S. household dust samples, according to a new study. The research adds to a growing body of evidence showing the dangers posed by exposure to chemicals we are exposed to on a daily basis. The chemicals come from a variety of household goods, including toys, cosmetics, personal care products, furniture, electronics, nonstick cookware, food packaging, floor coverings, some clothing (e.g., stain resistant), building materials, and cleaning products. How do the chemicals get into the dust? The chemicals can leach, migrate, abrade, or off-gas from the products, which winds up in the dust and results in human exposure. (That's right: vacuum a lot and wash your hands a lot, and try to avoid or cut back use of products with these chemicals,).jpg) There are some things we can do that are linked to living longer, such as not smoking and exercising regularly, but could reading books also have such an effect?
There are some things we can do that are linked to living longer, such as not smoking and exercising regularly, but could reading books also have such an effect?  Over the years I have read about some oils, especially lavender and tea tree oils, as having hormone altering (endocrine disrupting) effects when used over prolonged periods of time or when someone is "chronically exposed". Especially worrisome was the possible estrogenic effects of lavender oils in shampoos, lotions, and soaps on developing children - especially boys (prolonged use leading to the development of breasts in some boys!). I just read a recently published journal study (with very interesting comments at the end), and an article in WebMD about this same topic. The condition of early breast development is called prepubertal gynecomastia in boys and thelarche in girls.
Over the years I have read about some oils, especially lavender and tea tree oils, as having hormone altering (endocrine disrupting) effects when used over prolonged periods of time or when someone is "chronically exposed". Especially worrisome was the possible estrogenic effects of lavender oils in shampoos, lotions, and soaps on developing children - especially boys (prolonged use leading to the development of breasts in some boys!). I just read a recently published journal study (with very interesting comments at the end), and an article in WebMD about this same topic. The condition of early breast development is called prepubertal gynecomastia in boys and thelarche in girls. What happens to your brain when you stop exercising? The results of this
What happens to your brain when you stop exercising? The results of this  Studies are accumulating evidence that the hormone disrupting effects of compounds BPA (bisphenol A) and BPS (the common substitute for BPA) have numerous negative health effects in humans, including reproductive disorders. But now a second BPA substitute - BPSIP - is also being found in humans, and may be even more persistent than BPA and BPS. This is because they're all chemically similar, and all three are endocrine disruptors. This article points out that they have slightly different effects, and when we are exposed to more than one of them (which we are), then the health effects will be even more worrisome.
Studies are accumulating evidence that the hormone disrupting effects of compounds BPA (bisphenol A) and BPS (the common substitute for BPA) have numerous negative health effects in humans, including reproductive disorders. But now a second BPA substitute - BPSIP - is also being found in humans, and may be even more persistent than BPA and BPS. This is because they're all chemically similar, and all three are endocrine disruptors. This article points out that they have slightly different effects, and when we are exposed to more than one of them (which we are), then the health effects will be even more worrisome.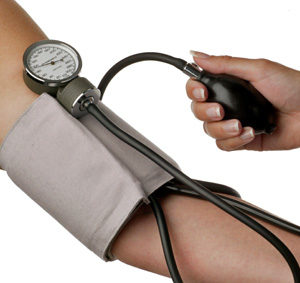 Can eating a vegetarian diet lower blood pressure? Both this review and other reviews of studies say YES, that those following vegetarian diets have a lower prevalence of hypertension. Overall, the mean prevalence of hypertension was 21% in those consuming a vegetarian diet and 29% in those consuming a nonvegetarian diet (the differences varied between studies).Those following a vegetarian diet also tended to have a healthier lifestyle. As the researchers point out: blood pressure medicine lowers blood pressure for one day, while lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, not smoking, limiting or avoiding alcohol) can lower blood pressure for life.
Can eating a vegetarian diet lower blood pressure? Both this review and other reviews of studies say YES, that those following vegetarian diets have a lower prevalence of hypertension. Overall, the mean prevalence of hypertension was 21% in those consuming a vegetarian diet and 29% in those consuming a nonvegetarian diet (the differences varied between studies).Those following a vegetarian diet also tended to have a healthier lifestyle. As the researchers point out: blood pressure medicine lowers blood pressure for one day, while lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, not smoking, limiting or avoiding alcohol) can lower blood pressure for life. Yikes! A good reason to lose weight now rather than years from now, and the importance of not ignoring a weight gain (you know, over the years as the pounds slowly creep up). The researchers found that for every 10 years of being overweight as an adult, there was an associated 7% increase in the risk for all obesity-related cancers. The degree of overweight (dose-response) during adulthood was important in the risk of developing cancer, especially for
Yikes! A good reason to lose weight now rather than years from now, and the importance of not ignoring a weight gain (you know, over the years as the pounds slowly creep up). The researchers found that for every 10 years of being overweight as an adult, there was an associated 7% increase in the risk for all obesity-related cancers. The degree of overweight (dose-response) during adulthood was important in the risk of developing cancer, especially for