 Loneliness or social isolation is a health risk that can increase the risk of chronic illness and premature death. Why? Loneliness leads to fight-or-flight stress signaling, which can ultimately affect the production of white blood cells. Essentially, lonely people had a less effective immune response and more inflammation than non-lonely people. The study was part of the Chicago Health, Aging, and Social Relations Study (CHASRS) and followed 144 people over 10 years. From Science Daily:
Loneliness or social isolation is a health risk that can increase the risk of chronic illness and premature death. Why? Loneliness leads to fight-or-flight stress signaling, which can ultimately affect the production of white blood cells. Essentially, lonely people had a less effective immune response and more inflammation than non-lonely people. The study was part of the Chicago Health, Aging, and Social Relations Study (CHASRS) and followed 144 people over 10 years. From Science Daily:
Loneliness triggers cellular changes that can cause illness, study shows
Loneliness is more than a feeling: For older adults, perceived social isolation is a major health risk that can increase the risk of premature death by 14 percent.
Now a team of researchers, including U Chicago psychologist and leading loneliness expert John Cacioppo, has released a study shedding new light on how loneliness triggers physiological responses that can ultimately make us sick. The paper.... shows that loneliness leads to fight-or-flight stress signaling, which can ultimately affect the production of white blood cells. The study examined loneliness in both humans and rhesus macaques, a highly social primate species.
Previous research from this group had identified a link between loneliness and a phenomenon they called "conserved transcriptional response to adversity" or CTRA. This response is characterized by an increased expression of genes involved in inflammation and a decreased expression of genes involved in antiviral responses. Essentially, lonely people had a less effective immune response and more inflammation than non-lonely people.
For the current study, the team examined gene expression in leukocytes, cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against bacteria and viruses. As expected, the leukocytes of lonely humans and macaques showed the effects of CTRA--an increased expression of genes involved in inflammation and a decreased expression of genes involved in antiviral responses. But the study also revealed several important new pieces of information about loneliness' effect on the body.
Next, the team investigated the cellular processes linking social experience to CTRA gene expression in rhesus macaque monkeys at the California National Primate Research Center, which had been behaviorally classified as high in perceived social isolation. Like the lonely humans, the "lonely like" monkeys showed higher CTRA activity. They also showed higher levels of the fight-or-flight neurotransmitter, norepinephrine.
Previous research has found that norepinephrine can stimulate blood stem cells in bone marrow to make more of a particular kind of immune cell--an immature monocyte that shows high levels of inflammatory gene expression and low levels of antiviral gene expression. Both lonely humans and "lonely like" monkeys showed higher levels of monocytes in their blood.
Taken together, these findings support a mechanistic model in which loneliness results in fight-or-flight stress signaling, which increases the production of immature monocytes, leading to up-regulation of inflammatory genes and impaired anti-viral responses. The "danger signals" activated in the brain by loneliness ultimately affect the production of white blood cells. The resulting shift in monocyte output may both propagate loneliness and contribute to its associated health risks.

 This past week there was discussion of the number of high school football players that die annually while playing football (at least 5). But the bigger risk - because it involves so many players - is the damage to brains that occurs from concussions and from just being hit in football. The response from football enthusiasts is that there are safeguards now - that football players don't play after a concussion until they "heal" (show no obvious symptoms). But do they really heal? And much of the damage is from repeated hits, without having a concussion (sub-concussive blows or hits), what about the damage from that?
This past week there was discussion of the number of high school football players that die annually while playing football (at least 5). But the bigger risk - because it involves so many players - is the damage to brains that occurs from concussions and from just being hit in football. The response from football enthusiasts is that there are safeguards now - that football players don't play after a concussion until they "heal" (show no obvious symptoms). But do they really heal? And much of the damage is from repeated hits, without having a concussion (sub-concussive blows or hits), what about the damage from that?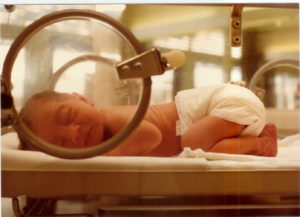 Another excellent reason to breastfeed premature infants - to increase the odds of preventing retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), which is the reason preemies can go blind. It occurs when blood vessels in the retinas of premature infants start to grow out of control. If the abnormal growth continues, the retinas detach, and this can cause blindness.
Another excellent reason to breastfeed premature infants - to increase the odds of preventing retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), which is the reason preemies can go blind. It occurs when blood vessels in the retinas of premature infants start to grow out of control. If the abnormal growth continues, the retinas detach, and this can cause blindness. Several people have recently asked me whether scented candles have any health effects. The answer is a big YES - they have many negative health effects, and so do other scented products such as air fresheners and dryer sheets (e,g, Bounce). All of them contain fragrances and other chemicals - all from petrochemicals (which means they are chemical products derived from petroleum). And yes - all 3 products are totally unnecessary, so ditch them for better health. View all of them as
Several people have recently asked me whether scented candles have any health effects. The answer is a big YES - they have many negative health effects, and so do other scented products such as air fresheners and dryer sheets (e,g, Bounce). All of them contain fragrances and other chemicals - all from petrochemicals (which means they are chemical products derived from petroleum). And yes - all 3 products are totally unnecessary, so ditch them for better health. View all of them as  The American Academy of Pediatrics released a new report that the overuse of antibiotics in animals poses a real health risk to children. Giving routine antibiotics to animals leads to antibiotic resistant bacteria - which means that antibiotics may not work when given to people. Most of the antibiotics sold in the U.S. each year - 80 percent- are used in animals that people than eat. The great majority of antibiotics given to animals are the same ones given to humans.The main way to ensure that the meat that you are purchasing is antibiotic-free is to
The American Academy of Pediatrics released a new report that the overuse of antibiotics in animals poses a real health risk to children. Giving routine antibiotics to animals leads to antibiotic resistant bacteria - which means that antibiotics may not work when given to people. Most of the antibiotics sold in the U.S. each year - 80 percent- are used in animals that people than eat. The great majority of antibiotics given to animals are the same ones given to humans.The main way to ensure that the meat that you are purchasing is antibiotic-free is to  People spend a lot of effort trying to repel mosquitos - because the bites are so annoying and because they spread serious diseases. New research looking at different mosquito repellents - both DEET and non-Deet ("natural") products - had interesting results. What was once thought effective in repelling mosquitoes doesn't work at all (vitamin B patch), and what was thought attractive to mosquitoes may actually repel them (floral scents), and the "natural" alternatives may or may not work. Also - the
People spend a lot of effort trying to repel mosquitos - because the bites are so annoying and because they spread serious diseases. New research looking at different mosquito repellents - both DEET and non-Deet ("natural") products - had interesting results. What was once thought effective in repelling mosquitoes doesn't work at all (vitamin B patch), and what was thought attractive to mosquitoes may actually repel them (floral scents), and the "natural" alternatives may or may not work. Also - the 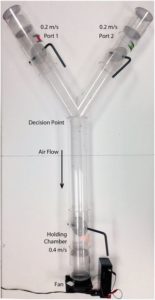 The Y-shaped tube used in the study.
The Y-shaped tube used in the study.  This study found that men who eat a lot of garlic (4 cloves in raw or capsule form) had a "more attractive" body odor to women. This is
This study found that men who eat a lot of garlic (4 cloves in raw or capsule form) had a "more attractive" body odor to women. This is  New research found that one course of
New research found that one course of  When suffering from cold symptoms or acute sinusitis, there are some products that work for nasal congestion, and thick phlegm and mucus.
When suffering from cold symptoms or acute sinusitis, there are some products that work for nasal congestion, and thick phlegm and mucus. 