New research is published every day, but only some studies are big research stories or game-changers. The following are what I consider some of the most memorable studies of 2018 – some in a good way, but some of the others have left me with a sense of horror. I think there will be follow-up research, so keep an eye out for more on these important topics.
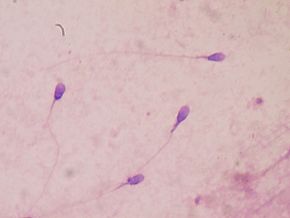 Are we heading toward a time in the not so distant future when all men are infertile? (Due to exposure to all the endocrine disruptors around us.) Will All Men Eventually Be Infertile? This was posted September 5, 2018.
Are we heading toward a time in the not so distant future when all men are infertile? (Due to exposure to all the endocrine disruptors around us.) Will All Men Eventually Be Infertile? This was posted September 5, 2018.
 Researchers are now seriously investigating and finding evidence that microbes may be causing Alzheimer’s disease. This approach is rapidly finding support in the medical field, and may lead to possible ways to treat or prevent the disease. Possible Herpes Virus Link to Alzheimer’s Disease was posted July 13, 2018, and Herpes Viruses and Alzheimer's Disease on June 22, 2018.
Researchers are now seriously investigating and finding evidence that microbes may be causing Alzheimer’s disease. This approach is rapidly finding support in the medical field, and may lead to possible ways to treat or prevent the disease. Possible Herpes Virus Link to Alzheimer’s Disease was posted July 13, 2018, and Herpes Viruses and Alzheimer's Disease on June 22, 2018.
 Type 2 Diabetes May Be Reversed With Weight Loss was posted August 10, 2018. This study and an earlier similar study from 2016 found that losing over 30 pounds over a short period can reverse type 2 diabetes - 46% in the 2018 study and 60% (in people who had it less than 10 years) in the earlier study.
Type 2 Diabetes May Be Reversed With Weight Loss was posted August 10, 2018. This study and an earlier similar study from 2016 found that losing over 30 pounds over a short period can reverse type 2 diabetes - 46% in the 2018 study and 60% (in people who had it less than 10 years) in the earlier study.
 More and more evidence is accumulating that certain diets are anti-inflammatory. Especially beneficial are diets rich in fruits, vegetables, seeds, nuts, legumes (beans), and whole grains - which also have a lot of fiber. This is exciting research because chronic low-grade inflammation is linked to a number of chronic diseases (heart disease, cancer, etc.). Fruits, Vegetables, and Whole Grains Lower Inflammation – posted August 1, 2018.
More and more evidence is accumulating that certain diets are anti-inflammatory. Especially beneficial are diets rich in fruits, vegetables, seeds, nuts, legumes (beans), and whole grains - which also have a lot of fiber. This is exciting research because chronic low-grade inflammation is linked to a number of chronic diseases (heart disease, cancer, etc.). Fruits, Vegetables, and Whole Grains Lower Inflammation – posted August 1, 2018.
 [Related to this last topic is one of the most eye-opening studies I have ever read on how what one eats has a quick effect on gut microbes and health of the gut (including inflammation of the colon): Changing Diet Has Big Effect On Colon Cancer Risk – posted April 28, 2015.]
[Related to this last topic is one of the most eye-opening studies I have ever read on how what one eats has a quick effect on gut microbes and health of the gut (including inflammation of the colon): Changing Diet Has Big Effect On Colon Cancer Risk – posted April 28, 2015.]
