 Hope your Labor Day was restful!
Hope your Labor Day was restful!
Record-breaking heat coming up this week in much of the United States.
Health, Microbes, and More

 Hope your Labor Day was restful!
Hope your Labor Day was restful!
Record-breaking heat coming up this week in much of the United States.

We can not get away from microplastics - the teeny, tiny plastic particles that are a result of plastics breaking up over time. They are everywhere, including the air over polar regions and in the air spewed out in the sea spray from waves.
Researchers sampled and analyzed air off the Norwegian coast up to the Arctic region. They found that all air samples contained microplastics. The plastic particles they found included polyester particles (from textiles), polystyrene, polypropylene, polyurethane, and tire wear particles (from driving and braking). Sources of the plastic particles came from both land (e.g., textiles, tire particles) and sea (e.g., boat paint).
Microplastics are plastic particles less than 5 mm (0.20 in) in length. Rain, water (e.g., seas, rivers), wind and air transport the plastic particles throughout the world. This microplastic pollution is of concern to all of us because we are breathing them in, and they are in the products we use (e.g., toothpaste), foods we eat, and the beverages we drink, including bottled water.
The big questions: What are the microplastic particles doing to us and wildlife? Are they getting into our organs? Are they causing chronic inflammation or other problems? Hint: Yes and yes, according to research. Even our lungs and blood.
From Science Daily: Oceans release microplastics into the atmosphere
Tiny plastic particles can be found in the sea air even far from coasts, according to a study recently published in the journal Nature Communications. The microplastics come from partly unexpected sources. ...continue reading "Microplastics Are Even In Ocean Waves and Air"

It turns out that even making minor adjustments to your usual diet can improve the gut microbiome (the community of bacteria, fungi, viruses living in the gut) within a few weeks. Two separate studies found that eating some peanuts daily or adding some herbs or spices to the foods you eat can improve the numbers of beneficial bacteria living in the gut.
 In the peanut study - eating or not eating peanuts didn't change the diversity or main types of bacteria living in the gut. But eating peanuts did increase the numbers of several beneficial species --Roseburia and Ruminococcaceae, which are butyrate producing bacteria (good!). The peanut group ate 28 grams of peanuts (1 ounce or about 33 peanuts) as a night-time snack for 6 weeks.
In the peanut study - eating or not eating peanuts didn't change the diversity or main types of bacteria living in the gut. But eating peanuts did increase the numbers of several beneficial species --Roseburia and Ruminococcaceae, which are butyrate producing bacteria (good!). The peanut group ate 28 grams of peanuts (1 ounce or about 33 peanuts) as a night-time snack for 6 weeks.
In the spice and herb study, adding a combination of spices and herbs to the diet for 4 weeks increased microbial diversity in the gut (good!), and also increased beneficial Ruminococcaceae numbers (good!) in persons at risk for heart disease. Faecalibacterium and Agathobacter numbers also increased (good!). A variety of dried spices and herbs (1/8 tsp, 3/4 tsp. or 1/1/2 tsp) were added to foods in the daily diet, and not taken as a capsule.
Dried spices added to foods in the spice and herb study included coriander, cumin, allspice, cinnamon, oregano, thyme, onion powder, garlic, ginger, rosemary, thyme, basil, black pepper, paprika, parsley, red pepper, etc. - 24 in all!
Bottom line: These studies agree with other research finding that eating peanuts (and all sorts of nuts, legumes), as well as adding spices and herbs to your foods is beneficial to the gut microbiome. They feed beneficial microbes in your gut, have all sorts of micronutrients, and they also have multitudes of microbes. A win-win.
From Science Daily: Peanuts and herbs and spices may positively impact gut microbiome
Adding a daily ounce of peanuts or about a teaspoon of herbs and spices to your diet may affect the composition of gut bacteria, an indicator of overall health, according to new research from Penn State. In two separate studies, nutritional scientists studied the effects of small changes to the average American diet and found improvements to the gut microbiome. ...continue reading "Adding Herbs and Spices To Your Foods Improves Gut Microbiome"

Today I saw some amazing photos that capture the moment of human ovulation. One can clearly see the egg emerging from a follicle on the ovary. Fertile women release one or more eggs each month.
The photos were taken in 2008 when Dr. Jacques Donnez was performing a hysterectomy on a 45 year old woman and saw that ovulation was occurring. The ovulation he witnessed took about 15 minutes.
By the way, it was the first time human ovulation was caught on camera.
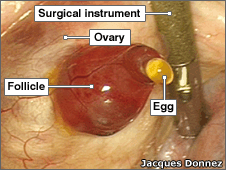
From June 11, 2008 BBC News: Ovulation moment caught on camera
A human egg has been filmed in close-up emerging from the ovary for the first time, captured by chance during a routine operation.
Fertile women release one or more eggs every month, but until now, only animal ovulation has been recorded in detail. ...continue reading "Observing Human Ovulation"
 There is nothing so refreshing as some cold ice cream on a hot summer day. But rather than viewing it as a guilty pleasure, research actually finds that it has health benefits!
There is nothing so refreshing as some cold ice cream on a hot summer day. But rather than viewing it as a guilty pleasure, research actually finds that it has health benefits!
Studies find that ice cream eaters have a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This is the same level of protection as eating yogurt.
What? Yup, studies found this health benefit, but it doesn't fit the prevailing dietary view of ice cream being an unhealthy food that should be avoided. So... the researchers of the studies didn't discuss the findings, and instead the results were hidden away. In other words, a case of bias.
By the way, cheese has had the same kind of bias against it for years (all that fat!), but finally the research finding health benefits is being discussed in the media (Consumer Reports).
Excerpts from The Atlantic: NUTRITION SCIENCE’S MOST PREPOSTEROUS RESULT Studies show a mysterious health benefit to ice cream. Scientists don’t want to talk about it.
Back in 2018, a Harvard doctoral student named Andres Ardisson Korat was presenting his research on the relationship between dairy foods and chronic disease to his thesis committee. One of his studies had led him to an unusual conclusion: Among diabetics, eating half a cup of ice cream a day was associated with a lower risk of heart problems. Needless to say, the idea that a dessert loaded with saturated fat and sugar might actually be good for you raised some eyebrows at the nation’s most influential department of nutrition. ...continue reading "Studies Find That Ice Cream Has Health Benefits"

A recent study found that indoor use of pesticides is associated with a higher risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Especially in women.
The researchers found that the longer the pesticide exposure time, the higher the risk, even among persons without any underlying risk factors such as diabetes and hypertension. This type of CKD, without known causes, is known as chronic kidney disease of unknown origins (CKDu).
CKDu has already been linked with outdoor use of pesticides, including glyphosate and malathion. This disease is on the rise globally, so studies like this one looking at indoor pesticides are important. When pesticides are applied indoors, persons living there are exposed (breathe in) pesticides for a long time. They do not break down like outdoors, where there is sunlight and rain.
The kidneys are one of the most important organs for filtering waste out of the human body. We need to protect them! One way is to use least-toxic Integrative Pest Management (IPM) when needing to control pests indoors (e.g., by caulking holes, using baits or traps).
Excerpts from Beyond Pesticides: Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Origins Linked To Indoor Pesticide Use, Disproportionately Affecting Women
A study published in PLOS ONE finds a pointed, positive association between chronic kidney disease (CKD) of unknown origins (CKDu) and the use of indoor pesticides. Longer exposure times have an especially detrimental impact on kidney function, even among individuals without underlying diseases like diabetes mellitus and hypertension. The innovation of this study’s purpose highlights the lack of exposure-related studies on kidney health outcomes associated with indoor pesticide use. ...continue reading "Indoor Use of Pesticides and Chronic Kidney Disease"

It is surprising that even now 15 states in the US allow corporal punishment (e.g., "paddling") as a form of discipline in schools. For even such minor offenses as being late or not having homework done. Yikes!
Paddling means hitting a child with a long wooden paddle. Mississippi is the number one state in the frequency of hitting (corporal punishment) children in schools - more than 3800 incidents of corporal punishment were reported in 2022-2023. Boys and black children are hit more than others.
So... these states think that hitting or beating a child by a person in authority is the way to "teach" them how to behave? Violence and aggression as a teaching tool? It's no surprise that studies find all sorts of negative outcomes from corporal punishment of children.
Excerpts from Washington Post: In over 15 states, schools can still paddle students as punishment
More than 15 states, mainly in the South, allow paddling or other physical discipline in schools. Among them, Mississippi has long topped the list, relying on the practice more than any other, according to federal data. Most schools in America — more than 90 percent — do not use corporal punishment.
...continue reading "Paddling In Schools Still Continues Today"
 Once again research finds that drinking sugar sweetened soft drinks or fruit drinks (not juices) is unhealthy. This time a study found that drinking one or more such beverages daily was linked to a higher rate of liver cancer and death from chronic liver diseases, when compared to those drinking 3 or fewer such drinks per month.
Once again research finds that drinking sugar sweetened soft drinks or fruit drinks (not juices) is unhealthy. This time a study found that drinking one or more such beverages daily was linked to a higher rate of liver cancer and death from chronic liver diseases, when compared to those drinking 3 or fewer such drinks per month.
This is an important finding because the majority of adults in the US consume one or more sweetened beverages daily! On the other hand, in this study drinking one or more artificially sweetened soda and drinks daily did not have an increased rate of liver cancer or death from chronic liver disease.
By the way, the researchers kept referring to the sweetener as sugar, but in reality the sweetener in (almost) all such beverages is high fructose corn syrup.
Excerpts from Science Daily: Women who consumed sugar sweetened beverage daily had higher risk of developing liver cancer and chronic liver disease
Approximately 65% of adults in the United States consume sugar sweetened beverages daily. Chronic liver disease is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide and can result in liver cancer and liver disease-related mortality. ...continue reading "Drinking Soda and Fruit Drinks Daily Linked to Risk of Liver Cancer and Death From Chronic Liver Diseases"
 We knew it was hot in July. Record breaking hot. Europe's climate monitoring organization (Copernicus Climate Change Service) announced this week that July was the Earth's hottest month on record. By a wide margin.
We knew it was hot in July. Record breaking hot. Europe's climate monitoring organization (Copernicus Climate Change Service) announced this week that July was the Earth's hottest month on record. By a wide margin.
The global average temperature for July was 62.51 degrees F (16.95 degrees C). The record for hottest month prior to this was July 2019. According to experts, July was the hottest month in about 120,000 years!
The global sea surface temperatures for July also broke historic records. The sea ice in the Antarctic broke the July record for below average sea ice. Do you see a pattern? Uh - oh. The world is really warming up...
According to a Climate Central report, more than 6.5 billion people (or more than 81% of people on Earth) experienced hotter temperatures in July than they would have without human-caused climate change.
Excerpts from World Meteorological Organization: July 2023 is set to be the hottest month on record
According to ERA5 data from the EU-funded Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S), the first three weeks of July have been the warmest three-week period on record and the month is on track to be the hottest July and the hottest month on record. These temperatures have been related to heatwaves in large parts of North America, Asia and Europe, which along with wildfires in countries including Canada and Greece, have had major impacts on people’s health, the environment and economies. ...continue reading "Scientists Report That July Was the Hottest Month On Record"
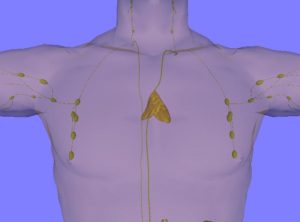
It turns out that a body part considered unimportant, and that frequently gets removed during operations - is actually important for adult health. This body part is the thymus. The thymus is frequently (routinely) removed during heart surgery for easier access to the heart and major blood vessels.
The thymus is an organ of the immune system within which T cells mature. For years the medical community regarded the thymus as only important before birth and during childhood, but "nonfunctional" in adults. A recent large study found that this view is wrong - that even in adults the thymus is important for immune and overall health.
Massachusetts General Hospital researchers found that after 5 years a higher risk of death from any cause (all cause mortality), cancer, and even autoimmune diseases among those who had thymus removal (thymectomy) versus those who had similar heart (cardiothoracic) surgery without thymus removal.
In other words, we need all our body parts! Even if the medical community doesn't quite understand (at this time) why we have them.
Excerpts from Medical Xpress: Study reveals unexpected importance of the thymus in adults
The thymus gland—which produces immune T cells before birth and during childhood— is often regarded as nonfunctional in adults, and it's sometimes removed during cardiac surgery for easier access to the heart and major blood vessels. ...continue reading "It Turns Out That The Thymus Is Important For Adult Health"