 A new report authored by dozens of scientists, health practitioners and children's health advocates is highlighting the (growing annually) evidence that many common and widely available chemicals endanger neurological development in fetuses and children of all ages. The chemicals contribute to such health problems as ADHD, autism spectrum disorders, lowered IQ, behavior disorders, and many other problems. Many of the chemicals have hormonal effects (endocrine disruptors) and interfere with normal hormonal activity. The chemicals of highest concern are all around us and are found in most pregnant women, their fetuses, and in growing children. In fact, in all of us.
A new report authored by dozens of scientists, health practitioners and children's health advocates is highlighting the (growing annually) evidence that many common and widely available chemicals endanger neurological development in fetuses and children of all ages. The chemicals contribute to such health problems as ADHD, autism spectrum disorders, lowered IQ, behavior disorders, and many other problems. Many of the chemicals have hormonal effects (endocrine disruptors) and interfere with normal hormonal activity. The chemicals of highest concern are all around us and are found in most pregnant women, their fetuses, and in growing children. In fact, in all of us.
Especially worrisome chemicals are: lead, mercury; organophosphate pesticides (used in agriculture and home gardens), phthalates (in medicines, plastics, and personal care products), flame retardants known as polybrominated diphenyl ethers (found in upholstered furniture, car seats), air pollutants produced by the combustion of wood and fossil fuels), and polychlorinated biphenyls (once used as coolants and lubricants in electrical equipment, but still pervasive). It is important to note that out of the thousands of chemicals that people are exposed to, that the great majority of chemicals are untested for neurodevelopmental effects.
Especially alarming is that the U.S. Centers for Disease Control found that 90% of pregnant women in the United States have detectable levels of 62 chemicals in their bodies, out of 163 chemicals for which the women were screened. This shows that we are exposed to mixtures of chemicals - not just to one chemical at a time. Unfortunately the substitutes for problematic chemicals are NO better than the originals, because they tend to be similar chemically. For example, the substitutes for BPA are just as bad, if not worse, than BPA (bisphenol A). And remember, we are exposed to mixtures of chemicals - not just to one chemical at a time.
The report criticizes current regulatory lapses that allow chemicals to be introduced into people's lives with little or no review of their effects on fetal and child health. "For most chemicals, we have no idea what they're doing to children's neurodevelopment," Professor Schantz (one of the signers of the report) said. "They just haven't been studied." So why aren't policymakers doing something? Why is industry dictating what we're exposed to? Why are chemicals innocent until proven guilty, and even then they're allowed to be used? Who is looking out for the ordinary person, and especially developing children?
From the journal Environmental Health Perspectives: Project TENDR: Targeting Environmental Neuro-Developmental Risks. The TENDR Consensus Statement
Children in America today are at an unacceptably high risk of developing neurodevelopmental disorders that affect the brain and nervous system including autism, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, intellectual disabilities, and other learning and behavioral disabilities. These are complex disorders with multiple causes—genetic, social, and environmental. The contribution of toxic chemicals to these disorders can be prevented.
Leading scientific and medical experts, along with children’s health advocates, came together in 2015 under the auspices of Project TENDR: Targeting Environmental Neuro-Developmental Risks to issue a call to action to reduce widespread exposures to chemicals that interfere with fetal and children’s brain development. Based on the available scientific evidence, the TENDR authors have identified prime examples of toxic chemicals and pollutants that increase children’s risks for neurodevelopmental disorders. These include chemicals that are used extensively in consumer products and that have become widespread in the environment. Some are chemicals to which children and pregnant women are regularly exposed, and they are detected in the bodies of virtually all Americans in national surveys conducted by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The vast majority of chemicals in industrial and consumer products undergo almost no testing for developmental neurotoxicity or other health effects.
Based on these findings, we assert that the current system in the United States for evaluating scientific evidence and making health-based decisions about environmental chemicals is fundamentally broken. To help reduce the unacceptably high prevalence of neurodevelopmental disorders in our children, we must eliminate or significantly reduce exposures to chemicals that contribute to these conditions. We must adopt a new framework for assessing chemicals that have the potential to disrupt brain development and prevent the use of those that may pose a risk. This consensus statement lays the foundation for developing recommendations to monitor, assess, and reduce exposures to neurotoxic chemicals.
The TENDR Consensus Statement is a call to action to reduce exposures to toxic chemicals that can contribute to the prevalence of neurodevelopmental disabilities in America’s children. The TENDR authors agree that widespread exposures to toxic chemicals in our air, water, food, soil, and consumer products can increase the risks for cognitive, behavioral, or social impairment, as well as specific neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) (Di Renzo et al. 2015; Gore et al. 2015; Lanphear 2015; Council on Environmental Health 2011). This preventable threat results from a failure of our industrial and consumer markets and regulatory systems to protect the developing brain from toxic chemicals. To lower children’s risks for developing neurodevelopmental disorders, policies and actions are urgently needed to eliminate or significantly reduce exposures to these chemicals.
We are witnessing an alarming increase in learning and behavioral problems in children. Parents report that 1 in 6 children in the United States, 17% more than a decade ago, have a developmental disability, including learning disabilities, ADHD, autism, and other developmental delays (Boyle et al. 2011). As of 2012, 1 in 10 (> 5.9 million) children in the United States are estimated to have ADHD (Bloom et al. 2013). As of 2014, 1 in 68 children in the United States has an autism spectrum disorder (based on 2010 reporting data) (CDC 2014).
Many toxic chemicals can interfere with healthy brain development, some at extremely low levels of exposure. Research in the neurosciences has identified “critical windows of vulnerability” during embryonic and fetal development, infancy, early childhood and adolescence (Lanphear 2015; Lyall et al. 2014; Rice and Barone 2000). During these windows of development, toxic chemical exposures may cause lasting harm to the brain that interferes with a child’s ability to reach his or her full potential.
The developing fetus is continuously exposed to a mixture of environmental chemicals (Mitro et al. 2015). A 2011 analysis of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) biomonitoring data found that 90% of pregnant women in the United States have detectable levels of 62 chemicals in their bodies, out of 163 chemicals for which the women were screened (Woodruff et al. 2011). Among the chemicals found in the vast majority of pregnant women are PBDEs, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHS), phthalates, perfluorinated compounds, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), perchlorate, lead and mercury (Woodruff et al. 2011). Many of these chemicals can cross the placenta during pregnancy and are routinely detected in cord blood or other fetal tissues.
The following list provides prime examples of toxic chemicals that can contribute to learning, behavioral, or intellectual impairment, as well as specific neurodevelopmental disorders such as ADHD or autism spectrum disorder: Organophosphate (OP) pesticides, PBDE flame retardants, combustion-related air pollutants, which generally include PAHs, nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter, and other air pollutants for which nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter are markers, lead, mercury, PCBs .
The United States has restricted some of the production, use and environmental releases of these particular chemicals, but those measures have tended to be too little and too late. We face a crisis from both legacy and ongoing exposures to toxic chemicals.....The examples of developmental neurotoxic chemicals that we list here likely represent the tip of the iceberg....Only a minority of chemicals has been evaluated for neurotoxic effects in adults. Even fewer have been evaluated for potential effects on brain development in children (Grandjean and Landrigan 2006, 2014). Further, toxicological studies and regulatory evaluation seldom address combined effects of chemical mixtures, despite evidence that all people are exposed to dozens of chemicals at any given time.
Some chemicals, like those that disrupt the endocrine system, present a concern because they interfere with the activity of endogenous hormones that are essential for healthy brain development. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) include many pesticides, flame retardants, fuels, and plasticizers. One class of EDCs that is ubiquitous in consumer products are the phthalates. These are an emerging concern for interference with brain development and therefore demand attention.
Under our current system, when a toxic chemical or category of chemicals is finally removed from the market, chemical manufacturers often substitute similar chemicals that may pose similar concerns or be virtually untested for toxicity. This practice can result in “regrettable substitution” whereby the cycle of exposures and adverse effects starts all over again. The following list provides examples of this cycle: When the federal government banned some uses of OP pesticides, manufacturers responded by expanding the use of neonicotinoid and pyrethroid pesticides. Evidence is emerging that these widely used classes of pesticides pose a threat to the developing brain (Kara et al. 2015; Richardson et al. 2015; Shelton et al. 2014).
When the U.S. Government reached a voluntary agreement with flame retardant manufacturers to stop making PBDEs, the manufacturers substituted other halogenated and organophosphate flame retardant chemicals. Many of these replacement flame retardants are similar in structure to other neurotoxic chemicals but have not undergone adequate assessment of their effects on developing brains. When the federal government banned some phthalates in children’s products, the chemical industry responded by replacing the banned chemicals with structurally similar new phthalates. These replacements are now under investigation for disrupting the endocrine system.
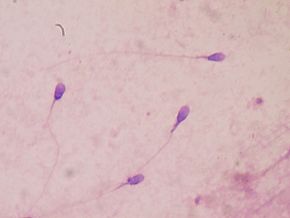 The following article in a popular magazine follows up on research that came out last year about the alarming steep decline in male sperm counts and sperm concentration over the past few decades. This is true for the U.S., Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and it is thought world wide. The article discusses the causes: environmental chemicals and plastics, especially those that are endocrine disruptors (they disrupt a person's hormones!). These chemicals are all around us, and we all have some in our bodies (but the amounts and types vary from person to person). Some examples of such chemicals are parabens, phthalates, BPA and BPA substitutes.
The following article in a popular magazine follows up on research that came out last year about the alarming steep decline in male sperm counts and sperm concentration over the past few decades. This is true for the U.S., Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and it is thought world wide. The article discusses the causes: environmental chemicals and plastics, especially those that are endocrine disruptors (they disrupt a person's hormones!). These chemicals are all around us, and we all have some in our bodies (but the amounts and types vary from person to person). Some examples of such chemicals are parabens, phthalates, BPA and BPA substitutes.
 Today I am posting the story of one person writing about how hard it is to reduce contaminants, that is, unwanted chemicals, in our bodies. The story is by Nicholas Kristof, who has been eating organic foods and trying his best to avoid endocrine (hormone) disrupting chemicals (such as BPA) for a number of years. But the analysis of his urine showed that he wasn't able to totally avoid them.
Today I am posting the story of one person writing about how hard it is to reduce contaminants, that is, unwanted chemicals, in our bodies. The story is by Nicholas Kristof, who has been eating organic foods and trying his best to avoid endocrine (hormone) disrupting chemicals (such as BPA) for a number of years. But the analysis of his urine showed that he wasn't able to totally avoid them. Both males and females should consider trying to lower their exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals (hormone disrupting chemicals) when contemplating pregnancy. These chemicals are found in many personal care, food packaging, and plastic products. They can interfere with natural hormone function and are linked to a wide assortment of health problems. Evidence (like this
Both males and females should consider trying to lower their exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals (hormone disrupting chemicals) when contemplating pregnancy. These chemicals are found in many personal care, food packaging, and plastic products. They can interfere with natural hormone function and are linked to a wide assortment of health problems. Evidence (like this  Many articles have been written about
Many articles have been written about  Recent research examined levels of endocrine disruptors called phthalates in people eating fast food. Researchers found evidence of a dose–response relationship between fast food intake and exposure to phthalates - the more one eats fast food, the more phthalates (actually metabolites of the phthalates) can be measured in the person's urine. Fast food consumers had higher urinary levels of the phthalates DEHP, DiNP, and BPA than those not consuming fast food (even though the differences in levels of BPA among groups were "non-significant"). This is of concern because these endocrine disruptors are linked to a
Recent research examined levels of endocrine disruptors called phthalates in people eating fast food. Researchers found evidence of a dose–response relationship between fast food intake and exposure to phthalates - the more one eats fast food, the more phthalates (actually metabolites of the phthalates) can be measured in the person's urine. Fast food consumers had higher urinary levels of the phthalates DEHP, DiNP, and BPA than those not consuming fast food (even though the differences in levels of BPA among groups were "non-significant"). This is of concern because these endocrine disruptors are linked to a  Ten chemicals suspected or known to harm human health are present in more than 90% of U.S. household dust samples, according to a new study. The research adds to a growing body of evidence showing the dangers posed by exposure to chemicals we are exposed to on a daily basis. The chemicals come from a variety of household goods, including toys, cosmetics, personal care products, furniture, electronics, nonstick cookware, food packaging, floor coverings, some clothing (e.g., stain resistant), building materials, and cleaning products. How do the chemicals get into the dust? The chemicals can leach, migrate, abrade, or off-gas from the products, which winds up in the dust and results in human exposure. (That's right: vacuum a lot and wash your hands a lot, and try to avoid or cut back use of products with these chemicals,)
Ten chemicals suspected or known to harm human health are present in more than 90% of U.S. household dust samples, according to a new study. The research adds to a growing body of evidence showing the dangers posed by exposure to chemicals we are exposed to on a daily basis. The chemicals come from a variety of household goods, including toys, cosmetics, personal care products, furniture, electronics, nonstick cookware, food packaging, floor coverings, some clothing (e.g., stain resistant), building materials, and cleaning products. How do the chemicals get into the dust? The chemicals can leach, migrate, abrade, or off-gas from the products, which winds up in the dust and results in human exposure. (That's right: vacuum a lot and wash your hands a lot, and try to avoid or cut back use of products with these chemicals,)