 An opinion piece in a journal raises the question of whether having some parasites in the gut is beneficial. We tend to think of parasites as harmful (and yes, some parasite species cause tremendous human suffering and death), but some others seem to exist harmlessly in humans. I'm posting this article because the authors raise the question of whether with progress (sanitation, antibiotics, a Western diet, etc.) we have also lost something beneficial to humans - one-celled organisms (protozoa) that are parasites. They are found in people living in undeveloped countries, but people in developed countries have usually few or none.
An opinion piece in a journal raises the question of whether having some parasites in the gut is beneficial. We tend to think of parasites as harmful (and yes, some parasite species cause tremendous human suffering and death), but some others seem to exist harmlessly in humans. I'm posting this article because the authors raise the question of whether with progress (sanitation, antibiotics, a Western diet, etc.) we have also lost something beneficial to humans - one-celled organisms (protozoa) that are parasites. They are found in people living in undeveloped countries, but people in developed countries have usually few or none.
Which leads to the question - is the loss of these parasites one of the reasons for the major increase in autoimmune disorders and such diseases as Crohn's disease and colitis? The answers to these questions are unknown at this time, so studies are needed. The authors point out that after millions of years of coevolution, the protists could be providing some beneficial effects to their human hosts - and that they may be part of a normal, healthy gut microbial community (microbiome).
As we know, studies show that in developed Western countries (as compared to undeveloped countries) there is lower microbial diversity in the gut - in other words, with industrialization comes lower bacterial diversity. But... higher microbial diversity is considered beneficial. Normally the human gut has hundreds of microbial species (bacteria, viruses, fungi) living in it and interacting. Some diseases or conditions result in alterations in these microbes, and even "microbial communities being out of whack" (dysbiosis). The authors of the paper give examples of how the presence of certain non-pathogenic protozoan species in the gut is linked to higher gut microbial diversity and with the presence of bacteria that are anti-inflammatory and beneficial.
KEEP IN MIND: Gut protozoa are one-celled organisms (called protists) that live in the gut as parasites. Numerous protozoa can inhabit the gastrointestinal tract of humans. According to a Tulane Univ. site "The majority of these protozoa are non-pathogenic commensals, or only result in mild disease", but some of these organisms can cause severe disease under certain conditions. [NOTE: commensal = characterized by a relationship in which one species is benefited while the other is unaffected]. In the following excerpts, a helminth refers to a parasitic worm, such as a fluke, tapeworm, or nematode.
Excerpts from Trends in Parasitology: Gut Protozoa: Friends or Foes of the Human Gut Microbiota?
The importance of the gut microbiota for human health has sparked a strong interest in the study of the factors that shape its composition and diversity.... We argue that protozoa, like helminths, represent an important factor to take into account when studying the gut microbiome, and that their presence – especially considering their long coevolutionary history with humans – may be beneficial. From this perspective, we examine the relationship between the protozoa and their hosts, as well as their relevance for public health.
The human gut microbiota spans the tree of life and includes bacteria, viruses, and eukaryotes such as fungi, helminths, and protozoa. ...The observation that the gut bacterial microbiome is less diverse in populations from industrialized countries, compared to nonindustrialized countries, has been mostly explained by differences in dietary fiber intake, food sterilization, and the use of antibiotics. Here, we propose that the decreased prevalence of helminths and gut protozoa in industrialized countries is partly responsible for this loss of bacterial diversity.
We argue, based on the knowledge of helminths, that some intestinal protozoa might have beneficial effects on their host through their influence on the gut bacterial microbiome. The role of protozoa in shaping the gut microbiome of healthy individuals remains, however, largely unrecognized. The mechanisms through which protozoa influence the gut bacteria – and the consequences for human health of their absence in developed countries – are poorly understood and call for further attention.
The question is therefore whether gut eukaryotes are simply parasites that are detrimental to human health or whether, on the contrary, they could provide, after millions of years of coevolution, some beneficial effects to their hosts. Historically, protozoa and helminths have been considered parasites and assumed to have a detrimental effect on the host organism. Indeed, foodborne and waterborne parasitic diseases are important worldwide, resulting in considerable morbidity and mortality. However, while the focus remains on pathogens that have been investigated from a parasitological point of view, the eukaryotic residents of the gut are often commensal (i.e., benefiting from interacting with the host without affecting it) or even beneficial.
For example, even though some helminths can cause severe illness, infections are often asymptomatic, probably reflecting a long coevolutionary history (since at least 500 million years) and tolerance of these parasites by humans. Similarly, although the best-known protozoan microorganisms found in the human gut are pathogens (i.e., Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia intestinalis, Entamoeba histolytica), it is important to remember that many protozoa, in particular Blastocystis spp., can be found with high prevalence in healthy populations, and are common (and likely ancient) members of healthy microbiomes. Indeed, although protozoan cysts are not as resistant to decay as helminth eggs, they can be found in coprolites, confirming that protozoa, like helminths, were part of our ancestral gut community.
Interestingly, recent findings also showed that the presence of commensal protozoa (Entamoeba spp. other than Entamoeba histolytica) was strongly associated with increased diversity and various shifts in composition of the gut bacterial microbiota in rural nonindustrialized populations. Higher diversity has also been found in subjects carrying Blastocystis spp., one of the few protozoa to be present at appreciable frequency in industrialized populations. These results suggest similarities between helminths and protozoa in their effect on the gut bacterial microbiome, and raise the possibility of a potentially beneficial effect of (some) protozoa on human health.
Here, we argue that some intestinal protozoan inhabitants could play an important, yet largely unrecognized, role in shaping the gut bacterial microbiota and in maintaining the host–microbe equilibrium, and they should be considered as ‘friends’ of the human gut.

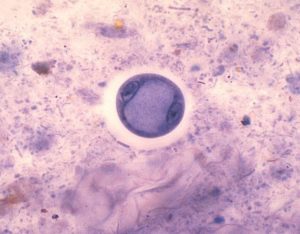
 Entamoeba coli - a non-pathogenic species that frequently lives as a commensal parasite in the human gastrointestinal tract. Credit: Wikipedia.
Entamoeba coli - a non-pathogenic species that frequently lives as a commensal parasite in the human gastrointestinal tract. Credit: Wikipedia.

 OK everyone - even if you sit all day at a desk job, the research is clear: try to get up and stretch or move a little every 30 minutes.
OK everyone - even if you sit all day at a desk job, the research is clear: try to get up and stretch or move a little every 30 minutes.  A major
A major  Another study finding that diet (what one eats) can work just as well as medications for a health condition - this time for one form of acid reflux disease. The
Another study finding that diet (what one eats) can work just as well as medications for a health condition - this time for one form of acid reflux disease. The  For years medicine has viewed cancer as a "malignant seed" and looked for ways to kill these seeds before they spread throughout the body (metastasis). This past week two provocative articles stresses that we should also look at the "environments" that the cancer cells grow in - that some environments in the person nourish and encourage the growth of cancer, while other environments suppress the growth of cancer and don't allow its spread.
For years medicine has viewed cancer as a "malignant seed" and looked for ways to kill these seeds before they spread throughout the body (metastasis). This past week two provocative articles stresses that we should also look at the "environments" that the cancer cells grow in - that some environments in the person nourish and encourage the growth of cancer, while other environments suppress the growth of cancer and don't allow its spread. For years medicine has viewed cancer as a "
For years medicine has viewed cancer as a " A study was just published by researchers at the University of California that reviewed the role of Lactobacillus bacteria in a variety of diseases and conditions. What was surprising was that while we generally think of Lactobacillus bacteria as beneficial, some studies suggest that in certain diseases or conditions they may not be. But it is unknown if in those cases whether they're causing harm or why they are there in increased amounts.
A study was just published by researchers at the University of California that reviewed the role of Lactobacillus bacteria in a variety of diseases and conditions. What was surprising was that while we generally think of Lactobacillus bacteria as beneficial, some studies suggest that in certain diseases or conditions they may not be. But it is unknown if in those cases whether they're causing harm or why they are there in increased amounts. Thunderstorm asthma
Thunderstorm asthma It seems like I can't stop writing about coffee (
It seems like I can't stop writing about coffee ( Two recent studies, both done in California, looked at different aspects of
Two recent studies, both done in California, looked at different aspects of