Many studies have discussed the short-term and long-term harm to the brain from playing tackle football, especially when starting the game at an early age (before the age of 12) , and from getting concussions and sub-concussions. But relatively little has been said about the possibility of similar harm from soccer (see post).
Finally a study looking at the practice of heading the ball in soccer - where yes, the person is directly hitting the soccer ball with his or her head, whether during a game or routine heading practice. Any harm from that? Yes. There were measurable brain function changes in both male and female young adults after heading a soccer ball 20 times during one practice session. While the changes ("short and long term memory function and corticomotor inhibition") were temporary, the researchers were concerned over possible long term brain effects (perhaps similar to those found in football players) when there are many practice sessions and soccer games, over many years. From Science Daily:
Heading a soccer ball causes instant changes to the brain
Researchers from the University of Stirling have explored the true impact of heading a soccer ball, identifying small but significant changes in brain function immediately after routine heading practice. The study from Scotland's University for Sporting Excellence published in EBioMedicine is the first to detect direct changes in the brain after players are exposed to everyday head impacts, as opposed to clinical brain injuries like concussion.
A group of soccer ball players headed a ball 20 times, fired from a machine designed to simulate the pace and power of a corner kick. Before and after the heading sessions, scientists tested players' brain function and memory. Increased inhibition in the brain was detected after just a single session of heading. Memory test performance was also reduced by between 41 and 67 per cent, with effects normalising within 24 hours. Whether the changes to the brain remain temporary after repeated exposure to a soccer ball and the long-term consequences of heading on brain health, are yet to be investigated.
Played by more than 250 million people worldwide, the 'beautiful game' often involves intentional and repeated bursts of heading a ball. In recent years the possible link between brain injury in sport and increased risk of dementia has focused attention on whether soccer ball heading might lead to long term consequences for brain health.
Cognitive neuroscientist Dr Magdalena Ietswaart from Psychology at the University of Stirling, said: "In light of growing concern about the effects of contact sport on brain health, we wanted to see if our brain reacts instantly to heading a soccer ball. Using a drill most amateur and professional teams would be familiar with, we found there was in fact increased inhibition in the brain immediately after heading and that performance on memory tests was reduced significantly.
"Although the changes were temporary, we believe they are significant to brain health, particularly if they happen over and over again as they do in soccer ball heading. With large numbers of people around the world participating in this sport, it is important that they are aware of what is happening inside the brain and the lasting effect this may have." In the study, scientists measured levels of brain function using a basic neuroscience technique called Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). (Original study)

 We all know that exercise is beneficial for health. Research suggests that exercising out in nature is best for several varied reasons - including that it
We all know that exercise is beneficial for health. Research suggests that exercising out in nature is best for several varied reasons - including that it  What happens to your brain when you stop exercising? The results of this
What happens to your brain when you stop exercising? The results of this  Again, another study showing the importance of lifestyle factors in the development of protein buildups in the brain that are associated with the onset of Alzheimer's disease. Specifically, the study found that each one of several lifestyle factors—a healthy body mass index, physical activity and a Mediterranean diet, were linked to lower levels of plaques and tangles on brain scans in people who already had mild memory changes, (but not dementia). Other posts discussing Mediterranean diet and brain health (brain volume, etc.) are
Again, another study showing the importance of lifestyle factors in the development of protein buildups in the brain that are associated with the onset of Alzheimer's disease. Specifically, the study found that each one of several lifestyle factors—a healthy body mass index, physical activity and a Mediterranean diet, were linked to lower levels of plaques and tangles on brain scans in people who already had mild memory changes, (but not dementia). Other posts discussing Mediterranean diet and brain health (brain volume, etc.) are  The
The 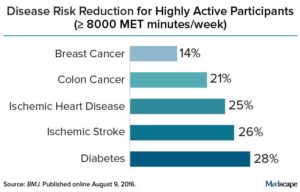 Credit: Medscape
Credit: Medscape Another study reporting health benefits of drinking tart cherry juice, specifically in speeding recovery following prolonged, repeat sprint activity (think soccer and rugby). The researchers found that after a prolonged, intermittent sprint activity, the cherry juice significantly lowered levels of Interleukin-6, a marker for inflammation and that there was a decrease in muscle soreness. The study participants drank the cherry juice (1 oz cherry juice concentrate mixed with 100 ml water) for several days before and several days after the sprint activity. Montmorency tart cherry juice is a
Another study reporting health benefits of drinking tart cherry juice, specifically in speeding recovery following prolonged, repeat sprint activity (think soccer and rugby). The researchers found that after a prolonged, intermittent sprint activity, the cherry juice significantly lowered levels of Interleukin-6, a marker for inflammation and that there was a decrease in muscle soreness. The study participants drank the cherry juice (1 oz cherry juice concentrate mixed with 100 ml water) for several days before and several days after the sprint activity. Montmorency tart cherry juice is a  A new study followed adults with meniscus tears (in the knee), who were randomly assigned to either exercise only or meniscus repair surgery (arthroscopic partial meniscectomy) only. They found that after 2 years there was no difference between those who just received exercise therapy compared to those who just received meniscus repair surgery. About 19% of the exercise only group decided to get surgery at some point, but the rest stayed in the exercise only group.
A new study followed adults with meniscus tears (in the knee), who were randomly assigned to either exercise only or meniscus repair surgery (arthroscopic partial meniscectomy) only. They found that after 2 years there was no difference between those who just received exercise therapy compared to those who just received meniscus repair surgery. About 19% of the exercise only group decided to get surgery at some point, but the rest stayed in the exercise only group. Everyone lifting light weights during exercise workouts will be heartened by a study that found that lifting
Everyone lifting light weights during exercise workouts will be heartened by a study that found that lifting