![]() We spend so much on health care, but the USA really lags behind other developed countries in quality of health care. The United States is ranked number 35 on the just released ranking of healthcare quality in 195 countries list. It is called the Healthcare Access and Quality Index, and is a highly regarded and much anticipated analysis, which was just published in the journal Lancet.
We spend so much on health care, but the USA really lags behind other developed countries in quality of health care. The United States is ranked number 35 on the just released ranking of healthcare quality in 195 countries list. It is called the Healthcare Access and Quality Index, and is a highly regarded and much anticipated analysis, which was just published in the journal Lancet.
How did such health care rankings start? In the late 1970s, some researchers first talked about the idea of “unnecessary, untimely deaths”, and they proposed a list of causes from which death should not occur if the person received "timely and effective medical care". This approach has been modified and extended over time, and now there is a list of 32 medical conditions looked at in 195 countries. The researchers looked at the death rate in each country for the diseases that can be avoided or can be effectively treated with proper medical care. Some of the diseases: diabetes, hypertension, some cancers, appendicitis, etc.
Virtually all the high ranking countries (the top 20) have universal health care, and yet they spend less on medical costs per person. Remember, when one can't afford the costs of medicines or treatments, and consequently dies - then that is the same as a "death panel" or "death sentence". So....is medical care a right for all or a privilege for some? From Medical Xpress:
Which countries have the best healthcare?
Neither Canada nor Japan cracked the top 10, and the United States finished a dismal 35th, according to a much anticipated ranking of healthcare quality in 195 countries, released Friday. Among nations with more than a million souls, top honours for 2015 went to Switzerland, followed by Sweden and Norway, though the healthcare gold standard remains tiny Andorra, a postage stamp of a country nestled between Spain (No. 8) and France (No. 15).
Iceland (No. 2), Australia (No. 6), Finland (No. 7), the Netherlands (No. 9) and financial and banking centre Luxembourg rounded out the first 10 finishers, according to a comprehensive study published in the medical journal The Lancet. Of the 20 countries heading up the list, all but Australia and Japan (No. 11) are in western Europe, where virtually every nation boasts some form of universal health coverage. The United States—where a Republican Congress wants to peel back reforms that gave millions of people access to health insurance for the first time—ranked below Britain, which placed 30th.
The Healthcare Access and Quality Index, based on death rates for 32 diseases that can be avoided or effectively treated with proper medical care, also tracked progress in each nation compared to the benchmark year of 1990. Virtually all countries improved over that period, but many—especially in Africa and Oceania—fell further behind others in providing basic care for their citizens. With the exceptions of Afghanistan, Haiti and Yemen, the 30 countries at the bottom of the ranking were all in sub-Saharan Africa, with the Central African Republic suffering the worst standards of all.
Furthermore, he added in a statement, the standard of primary care was lower in many nations than expected given levels of wealth and development.....Among rich nations, the worst offender in this category [underachievers] was the United States, which tops the world in per capita healthcare expenditure by some measures. Within Europe, Britain ranked well below expected levels.
The gap between actual and expected rating widened over the last quarter century in 62 of the 195 nations examined. "Overall, our results are a warning sign that heightened healthcare access and quality is not an inevitable product of increased development," Murray said.... The 32 diseases for which death rates were tracked included tuberculosis and other respiratory infections; illnesses that can be prevented with vaccines (diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus and measles); several forms of treatable cancer and heart disease; and maternal or neonatal disorders. [Original study.]

 Once again a great reason to exercise - a study found that adults with the highest levels of weekly physical activity had the longest telomeres, which are markers of overall health and aging. Think of it this way: we all age, but some people seem young for their age, while others seem old for their age. This study looked at differences among groups of people at the cellular level.
Once again a great reason to exercise - a study found that adults with the highest levels of weekly physical activity had the longest telomeres, which are markers of overall health and aging. Think of it this way: we all age, but some people seem young for their age, while others seem old for their age. This study looked at differences among groups of people at the cellular level.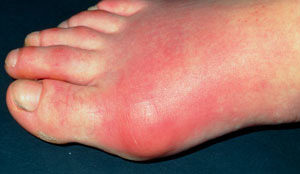 Gout is something that is not discussed that much, but it has been increasing in recent years and now afflicts about 3.9% of adults in the US. Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis, characterized by recurrent attacks of pain, tenderness, and swelling of a joint, frequently the joint of the big toe. It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood (known as hyperuricaemia).
Gout is something that is not discussed that much, but it has been increasing in recent years and now afflicts about 3.9% of adults in the US. Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis, characterized by recurrent attacks of pain, tenderness, and swelling of a joint, frequently the joint of the big toe. It is caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood (known as hyperuricaemia). This is a thought-provoking study that looked at environmental quality and cancer incidence in counties throughout the US. The researchers found that the more polluted the county, the higher the cancer incidence. An
This is a thought-provoking study that looked at environmental quality and cancer incidence in counties throughout the US. The researchers found that the more polluted the county, the higher the cancer incidence. An  The research finding of so many baby foods with elevated arsenic levels (above the legal limit) in the European Union made me wonder about arsenic standards in baby cereals in the US. It turns out that the US has "parallel" standards to the European Union. The EU has "maximum 0.1 milligrams of arsenic per kilogram of rice" (this standard has been in place since January 2016), and in 2016 the US the FDA proposed a "maximum allowed standard of 100 ppb (parts per billion)" in infant rice cereal.
The research finding of so many baby foods with elevated arsenic levels (above the legal limit) in the European Union made me wonder about arsenic standards in baby cereals in the US. It turns out that the US has "parallel" standards to the European Union. The EU has "maximum 0.1 milligrams of arsenic per kilogram of rice" (this standard has been in place since January 2016), and in 2016 the US the FDA proposed a "maximum allowed standard of 100 ppb (parts per billion)" in infant rice cereal. Another large recent study found that lowering sodium intakes (less than 2500 milligrams per day) wasn't linked to lower blood pressure. Over the course of 16 years, the researchers found that the study participants who consumed less than 2500 milligrams of sodium a day had higher blood pressure than participants who consumed higher amounts of sodium. However, the current 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends limiting sodium intake to 2,300 grams a day for healthy people. The researchers felt that based on recent studies with similar findings that the
Another large recent study found that lowering sodium intakes (less than 2500 milligrams per day) wasn't linked to lower blood pressure. Over the course of 16 years, the researchers found that the study participants who consumed less than 2500 milligrams of sodium a day had higher blood pressure than participants who consumed higher amounts of sodium. However, the current 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends limiting sodium intake to 2,300 grams a day for healthy people. The researchers felt that based on recent studies with similar findings that the  Good news! Once again a study has confirmed that eating fresh fruits is associated with a lower incidence of type 2 diabetes. And even better - there is a dose related relationship - the more one eats daily, the better. So don't worry about the "sugar content" of fruit - the key is to eat fruit (as well as vegetables) to lower the risk of getting diabetes. And if you have type 2 diabetes, it will lower the incidence of death and complications from diabetes.
Good news! Once again a study has confirmed that eating fresh fruits is associated with a lower incidence of type 2 diabetes. And even better - there is a dose related relationship - the more one eats daily, the better. So don't worry about the "sugar content" of fruit - the key is to eat fruit (as well as vegetables) to lower the risk of getting diabetes. And if you have type 2 diabetes, it will lower the incidence of death and complications from diabetes.