 Why are huge (42+ pound) bags of lawn chemicals being sold with foods in stores? Should stacked bags of pesticides ever be placed next to foods in stores? Is this legal? Why is this happening in warehouse stores that call themselves environmentally conscious and brag about carrying organic foods?
Why are huge (42+ pound) bags of lawn chemicals being sold with foods in stores? Should stacked bags of pesticides ever be placed next to foods in stores? Is this legal? Why is this happening in warehouse stores that call themselves environmentally conscious and brag about carrying organic foods?
Apparently the store does not recognize that the stacked bags of lawn chemicals (pesticides) are dangerous, that the bags can tear and spill pesticides, or that they always give off an awful chemical odor that can be smelled many aisles away. (This means we are breathing in those chemicals)
Why is it OK to place foods and enormous bags of pesticides in the same shopping cart, perhaps with children next to and handling the bags? (Note: I have personally seen this!) The pesticides should be sold in a separate area (like in Home Depot or Lowe's) or perhaps only in garden center. These pesticide products all say "Keep out of reach of children", to "avoid skin contact", and to "avoid inhaling". They are dangerous and do not belong in food stores.
The following photos were taken by me over the course of several years (2012 to 2015) in two Costco stores in NJ. The bags of "Turf Builder Winterguard Plus Weed Control" contain both fertilizer and pesticides and are commonly known as "Weed and Feed". Pesticides that kill weeds are also known as herbicides, and here the 2 pesticides (the active ingredients) are 2,4-D and mecoprop-p.
The first pesticide (2,4-D) was one of the the two pesticides found in Agent Orange used during the Vietnam War, and is linked to many serious health problems, including cancer in both people and dogs. (Note: scroll down for more information on these 2 pesticides).
Pesticides get into the body through the skin (dermal exposure) or eyes, through the mouth (ingesting it, including residues on foods), or through inhalation. Note that all odors represent an exposure to a chemical.
Pesticide products contain a number of ingredients – the “active ingredients” that targets the pest (weed or insect), and other ingredients that are just labeled "inert ingredients" or "other ingredients". Any one of them may produce a sickening odor. Odors also may be related to a breakdown product, a warning agent (a smelly substance added to make otherwise odorless products easier to detect), or a chemical added to the formula to hide a bad odor.
Currently, under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), pesticide manufacturers are only required to list the active ingredients in a pesticide, leaving consumers and applicators unaware of the possible toxics present in the inert or "other" ingredients of pesticide products. Pesticide manufacturers argue they cannot release information on inert ingredients because they are trade secrets, and if released, their products could be duplicated. Quite often inert ingredients constitute over 95% of the pesticide product, and can be as toxic as the active ingredients.
So.... what this means is that just by being able to smell the pesticide-fertilizers, we are being exposed to some chemicals through inhalation. And when this product is placed by foods, one doesn't smell food but instead inhales chemicals, perhaps the pesticides. These huge bags easily leak and spill (unlike small metal containers or cans). Leaking bags also result in shopping carts being contaminated with pesticides, as well as the store floor.
By placing the bags of pesticides next to foods, Costco is also sending the message to customers that the product is "safe", but that is incorrect. Pesticides that are dangerous (toxic) must be registered with the EPA. Harmless things don't have to be registered - toxic chemicals do.
And yes, a few years ago I contacted Costco management about this issue, but their response was to pooh-pooh my concerns, and that I must "be sensitive". And they continued as before. The following are some photos from 2012 to 2015 at 2 Costco warehouse stores.
 Next to refrigerated foods
Next to refrigerated foods
 Contains 2,4-D and Mecoprop-p
Contains 2,4-D and Mecoprop-p
 Next to bakery goods
Next to bakery goods
 By the meat
By the meat
2,4-D (or 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is a systemic herbicide (broadleaf weed-killer). It is linked to several cancers, especially non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and soft tissue sarcoma, and can have other serious health effects including endocrine disruption (disruption of hormones), thyroid effects, neurotoxicity (nervous system damage), and developmental and reproductive effects.
As the post of Oct.19, 2015 indicated, a person's exposure to 2,4-D can be measured in a person's urine. There is much still unknown about what constant low-level exposure to 2,4-D does to a fetus, developing child, or adult of any age.
Of big concern is that the use of 2,4-D is increasing in the USA because of the development of new genetically modified soybean and corn strains that are resistant to 2,4-D. Thus farmers are using increasingly large amounts of 2,4-D on these corn and soybean crops in an attempt to control weeds. And yes, this means consumers are eating more foods with 2,4-D residues. (Note: long-term effects unknown.)
Mecoprop-p is a chlorophenoxy herbicide that is used to control a variety of weeds. It is not as toxic as 2,4-D, but it also has various health effects.
Go to the excellent Beyond Pesticides site http://www.beyondpesticides.org/ for more information about all sorts of pesticides, resources, up-to-date information on pesticide laws, and more.

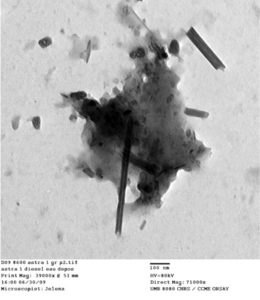 Carbon nanotubes (the long rods) and nanoparticles (the black clumps) appear in vehicle exhaust from tailpipes of cars in Paris.
Carbon nanotubes (the long rods) and nanoparticles (the black clumps) appear in vehicle exhaust from tailpipes of cars in Paris.
 Several studies have found that when children eat organic foods, especially fruits and vegetables, the amount of pesticides in their bodies declines significantly. Most organophosphorus pesticides have been phased out for residential use, but they are still widely used in agriculture, and so these pesticides are detected in both foods and people.
Several studies have found that when children eat organic foods, especially fruits and vegetables, the amount of pesticides in their bodies declines significantly. Most organophosphorus pesticides have been phased out for residential use, but they are still widely used in agriculture, and so these pesticides are detected in both foods and people. Once again, a study finds that foods are superior to supplements (here calcium supplements). It appears that eating foods rich in calcium has protective effects against kidney stones, but taking calcium supplements may result in kidney stone growth.
Once again, a study finds that foods are superior to supplements (here calcium supplements). It appears that eating foods rich in calcium has protective effects against kidney stones, but taking calcium supplements may result in kidney stone growth. A new
A new  A new study that tracked people more than 20 years found that a diet high in carotenoids - found in brightly colored fruits and vegetables (such as carrots, orange peppers, spinach, broccoli) - is linked to lower levels of macular degenaration (an age linked vision ailment).
A new study that tracked people more than 20 years found that a diet high in carotenoids - found in brightly colored fruits and vegetables (such as carrots, orange peppers, spinach, broccoli) - is linked to lower levels of macular degenaration (an age linked vision ailment).
 More and more studies are finding negative health effects from hormone disrupting chemicals (which we are exposed to every single day, and subsequently which are in all of us), such as parabens, phthalates, Bisphenol-A (BPA), and chemical substitutes for BPA such as Bisphenol-S (BPS) and BPF. The
More and more studies are finding negative health effects from hormone disrupting chemicals (which we are exposed to every single day, and subsequently which are in all of us), such as parabens, phthalates, Bisphenol-A (BPA), and chemical substitutes for BPA such as Bisphenol-S (BPS) and BPF. The