
Nowadays, the scientific view is to eat some nuts frequently for all sorts of health benefits. Recently, a study found that eating walnuts helps to lowers systemic inflammation (inflammation throughout the body), and in doing so reduces colon cancer risk.
The researchers said that the beneficial health effects are from ellagitannins, plant-derived polyphenol compounds, found in walnuts and pecans. Gut microbes convert the ellagitannins into anti-inflammatory urolithins.
Ellagitannins are also found in pomegranates, some berries (raspberries, blackberries, strawberries, cloudberries), and muscadine grapes. They are mainly metabolized by microbes in the colon. The consumption of foods containing ellagitannins has been associated with positive effects on many diseases (e.g., cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative syndromes, and cancer). Ellagitannins are antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cancer preventive.
From Medical Xpress: Walnut consumption curbs inflammation and may reduce colon cancer risk, clinical trial finds
There are new findings out about the benefits of eating walnuts. Results from a UConn School of Medicine clinical trial on the cover of the April edition of the journal Cancer Prevention Research show that walnuts improve systemic inflammation while also reducing colon cancer risk. ...continue reading "Walnuts, Gut Microbes, and Lower Levels of Inflammation"


 It's a sad fact, but Americans, even the richest ones, have a shorter life-span than their counterparts in Europe. A
It's a sad fact, but Americans, even the richest ones, have a shorter life-span than their counterparts in Europe. A
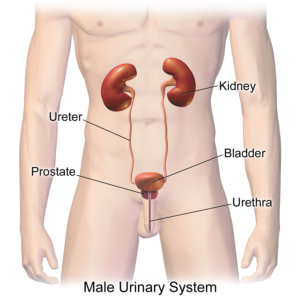
 What foods to avoid or to eat has long been debated in chronic kidney disease treatment. Traditionally, people with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have been advised to avoid a number of fruits and vegetables. In contrast, a recent
What foods to avoid or to eat has long been debated in chronic kidney disease treatment. Traditionally, people with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have been advised to avoid a number of fruits and vegetables. In contrast, a recent 
 Of course scented products (air fresheners,
Of course scented products (air fresheners,  There is much concern with the amount of highly or ultra-processed foods the typical American eats - over 50% of the calories eaten daily! A very good book about ultra-processed food is
There is much concern with the amount of highly or ultra-processed foods the typical American eats - over 50% of the calories eaten daily! A very good book about ultra-processed food is  The US is awash in pesticides - whether used on farms, in homes,
The US is awash in pesticides - whether used on farms, in homes,