Once again, bad news about ultra-processed foods. American adults eat so much ultra-processed food that it's now about 57% of their daily calories. It's because these foods are convenient, durable, available everywhere, taste good, and frequently are less expensive than whole foods.
Once again, bad news about ultra-processed foods. American adults eat so much ultra-processed food that it's now about 57% of their daily calories. It's because these foods are convenient, durable, available everywhere, taste good, and frequently are less expensive than whole foods.
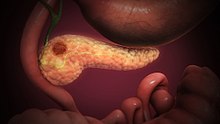
A large study found that eating lots of ultra-processed foods (e.g., prepackaged foods, fast foods) is associated with a higher risk of colon cancer in men. Specifically, a 29% higher risk when compared to men who ate the least ultra-processed foods.
This association was not found in women.
However, when the researchers looked at specific kinds or categories of ultra-processed foods that were eaten, they found differences in colorectal cancer risk. Higher consumption of meat/poultry/seafood based ready-to-eat-products and sugar sweetened beverages (soda!) was associated with a higher colorectal cancer risk in men. Higher consumption of ready-to-eat/heat mixed dishes was associated with colorectal cancer in women.
But interestingly, eating yogurt and dairy based desserts were negatively associated with colorectal cancer risk in women - it's as if they were protective. Perhaps the beneficial microbes in the dairy foods?
Ultra-processed foods are ready-to-eat or ready-to-heat foods made of little or no whole foods. Instead, they are mostly made of substances derived from foods. They typically have many added ingredients such as additives, artificial colors, preservatives, stabilizers, sugars, artificial sweeteners, salt, flavorings, and hydrogenated fats.
Examples are frozen meals, soft drinks, hot dogs, cold cuts, fast food, packaged foods (including cookies and cake), candies, instant soups, and sweet or savory packaged snacks.
Studies also show that ultra-processed foods cause negative or harmful changes in the gut microbiome (microbial community of bacteria, viruses, fungi). Higher consumption is associated with a higher risk of a number of chronic diseases and cancer.
From Science Daily - New study links ultra-processed foods and colorectal cancer in men
For many Americans, the convenience of pre-cooked and instant meals may make it easy to overlook the less-than-ideal nutritional information, but a team led by researchers at Tufts University and Harvard University hope that will change after recently discovering a link between the high consumption of ultra-processed foods and an increased risk of colorectal cancer. ...continue reading "Ultra-Processed Foods and Risk of Colorectal Cancer"

 It is very exciting whenever a study has good results in preventing cancer, especially if this is from simply eating certain foods. This recently occurred in a
It is very exciting whenever a study has good results in preventing cancer, especially if this is from simply eating certain foods. This recently occurred in a  More and more research over the past decade has stressed the importance of exercise for our health, but it turns out it is also important in slowing down tumor development. Yes - it actually reduces the growth of cancer.
More and more research over the past decade has stressed the importance of exercise for our health, but it turns out it is also important in slowing down tumor development. Yes - it actually reduces the growth of cancer. Americans spend enormous amounts of money on vitamins and mineral supplements in an effort to stay healthy or to improve their health. Unfortunately, unless a person has an actual vitamin or mineral deficiency, studies are just not finding health benefits. Sometimes there are even harms.
Americans spend enormous amounts of money on vitamins and mineral supplements in an effort to stay healthy or to improve their health. Unfortunately, unless a person has an actual vitamin or mineral deficiency, studies are just not finding health benefits. Sometimes there are even harms. What to do to maintain or improve health? Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes (beans), seeds, and nuts. Get enough exercise or physical activity. Don't smoke. Maintain a healthy weight.
What to do to maintain or improve health? Eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes (beans), seeds, and nuts. Get enough exercise or physical activity. Don't smoke. Maintain a healthy weight. Well, these were surprising study results, given that so many studies find that eating fish has such beneficial health effects. A recent
Well, these were surprising study results, given that so many studies find that eating fish has such beneficial health effects. A recent  Something surprising - having cancer is linked to a lower risk of Alzheimer's disease and a lower risk of neurodegenerative symptoms (e.g., memory loss) during their lifetimes.
Something surprising - having cancer is linked to a lower risk of Alzheimer's disease and a lower risk of neurodegenerative symptoms (e.g., memory loss) during their lifetimes. For years people have searched for ways to prevent cancer, which occurs significantly more with age. A
For years people have searched for ways to prevent cancer, which occurs significantly more with age. A  While very popular in many foods and beverages, some artificial sweeteners may increase the risk of developing cancer. The results of a large study found that ingesting some artificial sweeteners (especially aspartame and acesulfame-K) are associated with an increased risk of cancer.
While very popular in many foods and beverages, some artificial sweeteners may increase the risk of developing cancer. The results of a large study found that ingesting some artificial sweeteners (especially aspartame and acesulfame-K) are associated with an increased risk of cancer. There is a growing concern about what everyday exposures to phthalates in consumer products is doing to our health. For example, they're in plastic toys, plastic food containers, personal care products, and vinyl floors. The biggest concern is what these chemicals are doing to the most vulnerable among us - developing babies during pregnancy (gestational exposure), and children (childhood exposure).
There is a growing concern about what everyday exposures to phthalates in consumer products is doing to our health. For example, they're in plastic toys, plastic food containers, personal care products, and vinyl floors. The biggest concern is what these chemicals are doing to the most vulnerable among us - developing babies during pregnancy (gestational exposure), and children (childhood exposure).