 A second study was just published about the benefits of eating whole grains daily - again a significantly lower risk of premature death, and again the effects were dose-related. That is, the more whole grains eaten daily, the lower the risk of early death. Like the first study, this also was a review study. This study (published in BMJ) found that whole grain consumption was associated with a reduction in the risk for death from cancer, coronary heart disease (heart attack and stroke), respiratory disease, infectious disease, and diabetes.
A second study was just published about the benefits of eating whole grains daily - again a significantly lower risk of premature death, and again the effects were dose-related. That is, the more whole grains eaten daily, the lower the risk of early death. Like the first study, this also was a review study. This study (published in BMJ) found that whole grain consumption was associated with a reduction in the risk for death from cancer, coronary heart disease (heart attack and stroke), respiratory disease, infectious disease, and diabetes.
A slice of 100 percent whole grain bread contains about 16 grams of whole grains, and current U.S. dietary guidelines recommend 48 grams or more of whole grains daily, but this study suggests that eating even more whole grains daily is best (eating 90 grams of whole grains a day reduced the risk for mortality from all causes by 17 percent).
Grains are divided into two subgroups: whole grains and refined grains. Whole grains or foods made from them contain all the essential parts and naturally-occurring nutrients of the entire grain seed in their original proportions. This definition means that 100% of the original kernel – all of the bran, germ, and endosperm – must be present to qualify as a whole grain. Some whole grains are: whole wheat. barley. buckwheat, corn (including whole cornmeal and popcorn), millet, oats (including oatmeal), quinoa, brown rice, rye, sorghum, spelt, bulgur, and wild rice. From Eurekalert:
Seven servings of whole grains a day keep the doctor away
Eating three more portions of dietary fiber a day--say, two pieces of whole grain bread and a bowl of whole grain breakfast cereal--is associated with a lower risk for all cardiovascular diseases and for dying of cancer, diabetes, and respiratory and infectious diseases, a study just published in the BMJ has shown. The study is strong proof that consuming lots of whole grains is good for our health, says first author Dagfinn Aune, a PhD candidate at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology who is currently working at Imperial College, London.
....In general, the study showed that the higher the consumption, the better protected you are. "We saw the lowest risk among people who ate between seven and seven and a half servings of whole grain products a day, which was the highest intake across all the studies. This corresponds to 210-225 grams of whole grain products in fresh weight and about 70-75 grams of whole grains in dry weight, and is about the same as the health authorities in Norway and other Nordic countries recommend as the minimum daily allowance," says Aune.
The researchers' analyses showed fewer risk factors for people who consumed more bread and cereal with whole grains, as well as foods with added bran. On the other hand, people who ate a lot of white bread, rice or cereals with refined grains did not show reduced risk.
Nine studies with a total of more than 700,000 participants examined the risk for all types of cardiovascular disease and correlated cardiovascular deaths....The risk of dying prematurely from all causes was 18% lower for individuals who consumed a lot of whole grains compared to those who consumed lesser amounts, while three additional servings each day were associated with a 17% reduction in mortality. The risk for deaths associated with cancer (15%), respiratory diseases (22%), diabetes (51%) and infectious diseases (26%) was also lower the more whole grains individuals consumed.

 A recent
A recent  Surprising results (to me at least) from research comparing various diets and incidence of several cancers in 11,082 individuals in the Netherlands over a 20 year period. I expected the daily meat eaters to have higher rates of the 3 cancers studied, but no....
Surprising results (to me at least) from research comparing various diets and incidence of several cancers in 11,082 individuals in the Netherlands over a 20 year period. I expected the daily meat eaters to have higher rates of the 3 cancers studied, but no....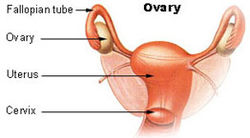 Another community of microbes found in humans in areas once thought to be sterile (without bacteria) - the ovaries and fallopian tubes in the female upper reproductive tract. And the interesting thing is that once again we see differences in the bacterial communities of areas with and without cancer (here the ovaries). From Science Daily:
Another community of microbes found in humans in areas once thought to be sterile (without bacteria) - the ovaries and fallopian tubes in the female upper reproductive tract. And the interesting thing is that once again we see differences in the bacterial communities of areas with and without cancer (here the ovaries). From Science Daily: New research looked at people who "aged successfully" over a 10 year period compared with those who were "suboptimal agers" or had died. The successful agers were less likely to smoke, and have higher intakes of fiber from fruits, breads, and cereals (primarily from rolled oats and whole grain breads), but not from vegetables. Successful aging was defined as including an absence of disability, depressive symptoms, cognitive impairment, respiratory symptoms, and chronic diseases including cancer, coronary artery disease, and stroke.
New research looked at people who "aged successfully" over a 10 year period compared with those who were "suboptimal agers" or had died. The successful agers were less likely to smoke, and have higher intakes of fiber from fruits, breads, and cereals (primarily from rolled oats and whole grain breads), but not from vegetables. Successful aging was defined as including an absence of disability, depressive symptoms, cognitive impairment, respiratory symptoms, and chronic diseases including cancer, coronary artery disease, and stroke.  As we know, chronic inflammation is linked to cancer and other diseases. It is long-term persistent low-grade inflammation, and it has a "wear and tear" effect on the body. What causes chronic inflammation? Being overweight or obese, sedentary lifestyle, Western (low fiber, high processed foods and meat) diet, chronic illnesses, viruses or bacteria (e.g., gum disease), smoking, air pollution, stress, excessive alcohol intake. It often does not have symptoms, but doctors can test for C-reactive protein levels (CRP), which increase when the body is inflamed. So you absolutely want to lower chronic inflammation if you can.
As we know, chronic inflammation is linked to cancer and other diseases. It is long-term persistent low-grade inflammation, and it has a "wear and tear" effect on the body. What causes chronic inflammation? Being overweight or obese, sedentary lifestyle, Western (low fiber, high processed foods and meat) diet, chronic illnesses, viruses or bacteria (e.g., gum disease), smoking, air pollution, stress, excessive alcohol intake. It often does not have symptoms, but doctors can test for C-reactive protein levels (CRP), which increase when the body is inflamed. So you absolutely want to lower chronic inflammation if you can.