 Lately the studies and articles about whether some alcohol consumption has health benefits (or not) have been mixed. But I am seeing patterns. Every one agrees that heavy alcohol consumption is unhealthy on many levels, but whether lower amounts are beneficial is disputed. Some of the studies show a J-shaped curve: regular consumption of low to moderate levels of wine (e.g., up to one to 2 glasses of wine, esp. red wine) seems best for health and is associated with low prevalence of various diseases (cardiovascular disease, diabetes, stroke, heart failure) and death, while total abstainers have a higher rate of health problems and mortality, and high levels of consumption (heavy drinkers) is linked to even higher levels of serious disease (heart disease, cancer) and death. Studies world-wide also find an alcohol dose-related link to cancer (the more one drinks, the higher the rates of various cancers). Earlier posts on alcohol consumption health effects are here and also here.
Lately the studies and articles about whether some alcohol consumption has health benefits (or not) have been mixed. But I am seeing patterns. Every one agrees that heavy alcohol consumption is unhealthy on many levels, but whether lower amounts are beneficial is disputed. Some of the studies show a J-shaped curve: regular consumption of low to moderate levels of wine (e.g., up to one to 2 glasses of wine, esp. red wine) seems best for health and is associated with low prevalence of various diseases (cardiovascular disease, diabetes, stroke, heart failure) and death, while total abstainers have a higher rate of health problems and mortality, and high levels of consumption (heavy drinkers) is linked to even higher levels of serious disease (heart disease, cancer) and death. Studies world-wide also find an alcohol dose-related link to cancer (the more one drinks, the higher the rates of various cancers). Earlier posts on alcohol consumption health effects are here and also here.
Adding to the complexity of this issue, low to moderate levels of wine consumption, especially red wine (up to 1 to 2 glasses of wine per day or several times a week), are part of the Mediterranean diet (linked to many health benefits, including longevity, lower rates of cancer and heart disease), and part of the diet of communities with many healthy centenarians ("Blue Zones"), according to The Blue Zones author Dan Buettner.
Perhaps part of the problem with reviews of the studies is that what is "light to moderate drinking" varies from study to study - is it 1/2 glass or 1 glass daily or several times a week, or 2 or 3 glasses daily, or even more? People tend to underestimate what they drink when asked. There also is the issue of hard liquor/spirits (which recent studies find to have more negative health effects such as higher cancer mortality) vs wine or beer, and also if one drinks a little each day or engages in binge or episodic drinking - all have different health effects. The CDC posts on its web-site: that moderate alcohol consumption is defined as having up to 1 drink per day for women and up to 2 drinks per day for men (this means no more than 7 drinks a week for a woman, and 14 for men). The Mayo Clinic defines a drink as one 12 oz. beer, 5 oz. of wine or 1.5 oz. of 80-proof spirits. I'm posting some of the studies and articles gathering recent headlines.
This was interesting in that 2 studies compared drinking low levels (1 daily wine glass) of white wine vs red wine. In the second study both wine groups also had significantly improved triglyceride levels, and the white wine group had significantly decreased fasting plasma glucose levels (better glucose control). From Washington Post: White wines may be just as good for you as red (in some ways, at least)
The short answer is that the evidence supporting white wine's health benefits, while still limited, is growing. While previous studies on the elixir have been mostly focused on testing in animals or on testing the components of the drink itself, scientists have recently reported on two randomized clinical trials that found good news for white wine enthusiasts.
The first study, called In Vino Veritas (In Wine, Truth) involved tracking 146 subjects half of whom drank pinot noir, and half of whom drank a white chardonnay-pinot over a year. The researchers reported at a European Society of Cardiology meeting last year that those who worked out twice per week and drank wine — either kind — saw a significant improvement in cholesterol levels.
The second, published Monday in the Annals of Internal Medicine, had a similar design. Researchers in Israel recruited 224 volunteers with diabetes 2 to drink 150 mL of either white wine, red wine or mineral water (the control) with dinner every day for two years. They were encouraged to eat a Mediterranean diet, which includes mostly plant-based foods and replaces butter with olive oil, but their caloric intake was not restricted.
The results were compelling: Drinking a glass of red wine (but not white wine) every day appeared to improve cardiac health and cholesterol management. But both red and white wine seemed to improve glucose control in some patients. Full of the same plant flavonoids in red wine that are thought to have a protective effect, white wine has been studied significantly less despite some promising initial findings. White wine has been shown by researchers at the University of Barcelona to be higher in antioxidants and has been associated with weight loss and anti-aging effects. Interestingly, researchers say no material differences were identified in blood pressure, adiposity, liver function, drug therapy, symptoms or quality of life among those who drank red wine, white wine or mineral water except for one thing. Sleep quality, it seems, improved in both wine groups.
A more detailed discussion of the above study (diabetics consuming either red wine, white wine, or mineral water). From Medscape: Red Wine, White Wine Improve Cardiometabolic Risk Markers in Diabetics, Says 2-Year Trial
These results don't match up with all the other studies showing cardiovascular benefits from small to moderate levels of alcohol consumption. From Washington Post: Surprising finding from heart study: Moderate drinking may have ‘cardiotoxic’ effects in elderly hearts
In a study of 4,466 people between the ages of 71 and 81, researchers found that even a limited alcohol intake of two or more servings a day for men and one or more for women was associated with subtle alterations in cardiac structure and function. Of those affected, the men experienced enlarged left ventricle walls while the women saw a small reduction in heart function.....elderly women appeared to be more susceptible to the cardiotoxic effects of alcohol.
The study appears to contradict or at least provide a new perspective on previous research. According to the Harvard School of Public Health, more than 100 prospective studies show that moderate drinking is associated with a lower risk of heart attack and other cardiovascular issues. "The effect is fairly consistent, corresponding to a 25 percent to 40 percent reduction in risk," according to a summary of literature its researchers put together.
More support for low levels/moderate alcohol intake, but not for smoking and heavy alcohol use, or even for totally abstaining from alcohol. from Science Daily: Smoking, heavy alcohol use are associated with epigenetic signs of aging
Cigarette smoking and heavy alcohol use cause epigenetic changes to DNA that reflect accelerated biological aging in distinct, measurable ways, according to research....They found that all levels of exposure to smoke were associated with significantly premature aging. Interestingly, moderate alcohol use -- about one to two drinks per day -- was correlated with the healthiest aging, while very low and high consumption were linked to accelerated aging.
From Science Daily: Women with moderate beer consumption run lower risk of heart attack
Women who drink beer at most once or twice per week run a 30 percent lower risk of heart attack, compared with both heavy drinkers and women who never drink beer. These are the findings of a Swedish study which has followed 1,500 women over a period of almost 40 years....High spirits consumption was associated with increased risk of cancer mortality. (NOTE: The original study is in the Scandinavian Journal of Health Care - In addition, they found that women who sometimes drank wine had a lower risk of developing diabetes compared with the other two groups. Also: a tendency for increased mortality was found in women who had never drunk alcohol.)
However, a September 2015 Medscape article said that the picture is complex (some alcohol linked to better cardiovascular health, but that alcohol consumption is linked to cancer). They found the greatest negative effects in low income countries where there are higher rates of heavy alcohol use. Alcohol Ups Mortality and Cancer Risk; No Net Benefit
Last year Medscape published an article pointing out the conclusions of the 2014 World Cancer Report (WCR), issued by the World Health Organization's International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). The main conclusion: the rate of cancer from alcohol consumption is dose dependent - the more alcohol a person drinks, the higher the risk of cancer. Back in 1988 , the IARC labeled alcohol a carcinogen. However, what is "light to moderate drinking" varies from study to study, and perhaps light and moderate levels need to be separated out. From Medscape: No Amount of Alcohol Is Safe
The more alcohol that a person drinks, the higher the risk. The alcohol/cancer link has been strengthened by the finding of a dose/response relationship between alcohol consumption and certain cancers. A causal relationship exists between alcohol consumption and cancers of the mouth, pharynx, larynx, esophagus, colon-rectum, liver, and female breast; a significant relationship also exists between alcohol consumption and pancreatic cancer.
But surely, light drinking doesn't cause or contribute to cancer? Apparently, it does. In a meta-analysis of 222 studies comprising 92,000 light drinkers and 60,000 nondrinkers with cancer, light drinking was associated with risk for oropharyngeal cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and female breast cancer.From this meta-analysis, it was estimated that in 2004 worldwide, 5000 deaths from oropharyngeal cancer, 24,000 from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and 5000 from breast cancer were attributable to light drinking. Light drinking was not associated with cancer of the colon-rectum, liver, or larynx.
However, a caveat is in order here. When alcohol use is self-reported, respondents might underestimate, or underreport, their actual alcohol intake. This can result in finding associations between cancer and light to moderate drinking, when in reality, alcohol intake is much higher.
Drink coffee daily - 3 to 5 cups of either regular or decaffeinated - and live longer by lowering your risk of premature death from cardiovascular disease, neurological disease, type 2 diabetes, and suicide. Yes, it was an observational study, but the results are similar to what other studies are finding. From Medical Xpress:

 New research found that negative health effects - 35% increased risk of cardiovascular problems (coronary heart disease, heart attacks, strokes) are when the vitamin D levels are really low (under 15 nanograms per milliliter). Currently many doctors recommend optimal levels for health as somewhere between 35 to 40 ng/ml. One
New research found that negative health effects - 35% increased risk of cardiovascular problems (coronary heart disease, heart attacks, strokes) are when the vitamin D levels are really low (under 15 nanograms per milliliter). Currently many doctors recommend optimal levels for health as somewhere between 35 to 40 ng/ml. One  This study showed that children reducing sugar consumption (but not fruits), and without reducing calories, after 10 days improved all sorts of metabolic health markers: blood pressure, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, liver function, fasting blood glucose, and insulin levels. As one of the researchers said: "I have never seen results as striking or significant in our human studies; after only nine days of fructose (sugar) restriction, the results are dramatic and consistent from subject to subject." Once again, not all calories are the same.
This study showed that children reducing sugar consumption (but not fruits), and without reducing calories, after 10 days improved all sorts of metabolic health markers: blood pressure, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, liver function, fasting blood glucose, and insulin levels. As one of the researchers said: "I have never seen results as striking or significant in our human studies; after only nine days of fructose (sugar) restriction, the results are dramatic and consistent from subject to subject." Once again, not all calories are the same. Another study providing evidence that the Mediterranean diet is good for the brain. In elderly dementia-free adults (mean age 80 years) - those that generally followed a Mediterranean diet (higher adherence) had a
Another study providing evidence that the Mediterranean diet is good for the brain. In elderly dementia-free adults (mean age 80 years) - those that generally followed a Mediterranean diet (higher adherence) had a  Several studies have found that when children eat organic foods, especially fruits and vegetables, the amount of pesticides in their bodies declines significantly. Most organophosphorus pesticides have been phased out for residential use, but they are still widely used in agriculture, and so these pesticides are detected in both foods and people.
Several studies have found that when children eat organic foods, especially fruits and vegetables, the amount of pesticides in their bodies declines significantly. Most organophosphorus pesticides have been phased out for residential use, but they are still widely used in agriculture, and so these pesticides are detected in both foods and people.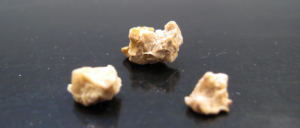 Once again, a study finds that foods are superior to supplements (here calcium supplements). It appears that eating foods rich in calcium has protective effects against kidney stones, but taking calcium supplements may result in kidney stone growth.
Once again, a study finds that foods are superior to supplements (here calcium supplements). It appears that eating foods rich in calcium has protective effects against kidney stones, but taking calcium supplements may result in kidney stone growth. A new study that tracked people more than 20 years found that a diet high in carotenoids - found in brightly colored fruits and vegetables (such as carrots, orange peppers, spinach, broccoli) - is linked to lower levels of macular degenaration (an age linked vision ailment).
A new study that tracked people more than 20 years found that a diet high in carotenoids - found in brightly colored fruits and vegetables (such as carrots, orange peppers, spinach, broccoli) - is linked to lower levels of macular degenaration (an age linked vision ailment).
 More and more studies are finding negative health effects from hormone disrupting chemicals (which we are exposed to every single day, and subsequently which are in all of us), such as parabens, phthalates, Bisphenol-A (BPA), and chemical substitutes for BPA such as Bisphenol-S (BPS) and BPF. The
More and more studies are finding negative health effects from hormone disrupting chemicals (which we are exposed to every single day, and subsequently which are in all of us), such as parabens, phthalates, Bisphenol-A (BPA), and chemical substitutes for BPA such as Bisphenol-S (BPS) and BPF. The