 A newly published study reviewed 61 studies that looked at daily tree nut consumption on cardiovascular risk factors and found many health benefits. Tree nut (walnuts, almonds, pistachios, macadamia nuts, pecans, cashews, hazelnuts, and Brazil nuts) consumption lowers total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and ApoB, the primary protein in LDL cholesterol. It appeared that nut dose is more important than nut type in lowering cholesterol. The beneficial health effects are greater at about 60 grams (about 2 oz or 2 servings) or more nuts consumed per day, but positive health effects are also found at one serving per day. Five studies found that 100 g nuts per day lowered concentrations of LDL cholesterol by up to 35 mg/dL - an effect size comparable to some statin regimens.
A newly published study reviewed 61 studies that looked at daily tree nut consumption on cardiovascular risk factors and found many health benefits. Tree nut (walnuts, almonds, pistachios, macadamia nuts, pecans, cashews, hazelnuts, and Brazil nuts) consumption lowers total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and ApoB, the primary protein in LDL cholesterol. It appeared that nut dose is more important than nut type in lowering cholesterol. The beneficial health effects are greater at about 60 grams (about 2 oz or 2 servings) or more nuts consumed per day, but positive health effects are also found at one serving per day. Five studies found that 100 g nuts per day lowered concentrations of LDL cholesterol by up to 35 mg/dL - an effect size comparable to some statin regimens.
Tree nuts are rich in unsaturated fats, soluble fiber, antioxidants, and phytosterols, which produce beneficial effects on serum lipids, blood pressure, and inflammation. Most studies have looked at walnut and almond consumption, but studies found positive benefits for all types of nuts consumed. From Medical Xpress:
Study finds tree nut consumption may lower risk of cardiovascular disease
A new study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that consuming tree nuts, such as walnuts, may lower the risk of cardiovascular disease. After conducting a systematic review and meta-analysis of 61 controlled trials, one of the authors, Michael Falk, PhD, Life Sciences Research Organization, found that consuming tree nuts lowers total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and ApoB, the primary protein found in LDL cholesterol. These are key factors that are used to evaluate a person's risk of cardiovascular disease. Walnuts were investigated in 21 of the 61 trials, more than any other nut reviewed in this study.
"Our study results further support the growing body of research that tree nuts, such as walnuts, can reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases," said Dr. Falk. "Tree nuts contain important nutrients such as unsaturated fats, protein, vitamins and minerals. Walnuts are the only nut that provide a significant amount (2.5 grams per one ounce serving) of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), the plant-based form of omega-3s."
Beyond finding that tree nuts lower total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL cholesterol and ApoB, researchers also found that consuming at least two servings (two ounces) per day of tree nuts, such as walnuts, has stronger effects on total cholesterol and LDL. Additionally, results showed that tree nut consumption may be particularly important for lowering the risk of heart disease in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Of 1,301 articles surveyed, 61 trials met eligibility criteria for this systematic review and meta-analysis, totaling 2,582 unique participants. Trials directly provided nuts to the intervention group rather than relying solely on dietary advice to consume nuts. The dose of nuts varied from 5 to 100 g/day and most participants followed their typical diet.

 Data from 2 huge studies was analyzed and found that vigorous exercise and other healthy habits seems to cut the chance of developing aggressive and lethal prostate cancer up to 68 percent in men over 60. The beneficial lifestyle habits are: weekly vigorous exercise or activity to the point of sweating, at least 7 servings of tomatoes a week, at least one serving of fatty fish per week, reduced intake of processed meat, and being a long-term non-smoker.
Data from 2 huge studies was analyzed and found that vigorous exercise and other healthy habits seems to cut the chance of developing aggressive and lethal prostate cancer up to 68 percent in men over 60. The beneficial lifestyle habits are: weekly vigorous exercise or activity to the point of sweating, at least 7 servings of tomatoes a week, at least one serving of fatty fish per week, reduced intake of processed meat, and being a long-term non-smoker. Several people have recently asked me whether scented candles have any health effects. The answer is a big YES - they have many negative health effects, and so do other scented products such as air fresheners and dryer sheets (e,g, Bounce). All of them contain fragrances and other chemicals - all from petrochemicals (which means they are chemical products derived from petroleum). And yes - all 3 products are totally unnecessary, so ditch them for better health. View all of them as
Several people have recently asked me whether scented candles have any health effects. The answer is a big YES - they have many negative health effects, and so do other scented products such as air fresheners and dryer sheets (e,g, Bounce). All of them contain fragrances and other chemicals - all from petrochemicals (which means they are chemical products derived from petroleum). And yes - all 3 products are totally unnecessary, so ditch them for better health. View all of them as  The American Academy of Pediatrics released a new report that the overuse of antibiotics in animals poses a real health risk to children. Giving routine antibiotics to animals leads to antibiotic resistant bacteria - which means that antibiotics may not work when given to people. Most of the antibiotics sold in the U.S. each year - 80 percent- are used in animals that people than eat. The great majority of antibiotics given to animals are the same ones given to humans.The main way to ensure that the meat that you are purchasing is antibiotic-free is to
The American Academy of Pediatrics released a new report that the overuse of antibiotics in animals poses a real health risk to children. Giving routine antibiotics to animals leads to antibiotic resistant bacteria - which means that antibiotics may not work when given to people. Most of the antibiotics sold in the U.S. each year - 80 percent- are used in animals that people than eat. The great majority of antibiotics given to animals are the same ones given to humans.The main way to ensure that the meat that you are purchasing is antibiotic-free is to  People spend a lot of effort trying to repel mosquitos - because the bites are so annoying and because they spread serious diseases. New research looking at different mosquito repellents - both DEET and non-Deet ("natural") products - had interesting results. What was once thought effective in repelling mosquitoes doesn't work at all (vitamin B patch), and what was thought attractive to mosquitoes may actually repel them (floral scents), and the "natural" alternatives may or may not work. Also - the
People spend a lot of effort trying to repel mosquitos - because the bites are so annoying and because they spread serious diseases. New research looking at different mosquito repellents - both DEET and non-Deet ("natural") products - had interesting results. What was once thought effective in repelling mosquitoes doesn't work at all (vitamin B patch), and what was thought attractive to mosquitoes may actually repel them (floral scents), and the "natural" alternatives may or may not work. Also - the 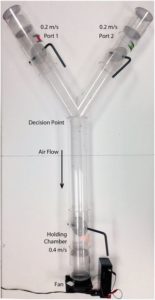 The Y-shaped tube used in the study.
The Y-shaped tube used in the study.  This study found that men who eat a lot of garlic (4 cloves in raw or capsule form) had a "more attractive" body odor to women. This is
This study found that men who eat a lot of garlic (4 cloves in raw or capsule form) had a "more attractive" body odor to women. This is  New research found that one course of
New research found that one course of  New research found that negative health effects - 35% increased risk of cardiovascular problems (coronary heart disease, heart attacks, strokes) are when the vitamin D levels are really low (under 15 nanograms per milliliter). Currently many doctors recommend optimal levels for health as somewhere between 35 to 40 ng/ml. One
New research found that negative health effects - 35% increased risk of cardiovascular problems (coronary heart disease, heart attacks, strokes) are when the vitamin D levels are really low (under 15 nanograms per milliliter). Currently many doctors recommend optimal levels for health as somewhere between 35 to 40 ng/ml. One  Nice update from a large crowd sourced study I posted about
Nice update from a large crowd sourced study I posted about